Global, regional, and national burden and risk factors of ischemic heart disease, 1990-2021: an analysis of the global burden of disease study
- PMID: 40352854
- PMCID: PMC12061725
- DOI: 10.3389/fpubh.2025.1563631
Global, regional, and national burden and risk factors of ischemic heart disease, 1990-2021: an analysis of the global burden of disease study
Abstract
Background: With a rapidly growing and aging world population, ischemic heart disease (IHD) remains a major burden. This study aimed to reassess the prevalence trend of IHD from 1990 to 2021 from multiple dimensions to improve the shortcomings of the existing studies and provide a solid scientific basis for policymakers.
Methods: This study extracted data on the prevalence, incidence, mortality, disability-adjusted life years (DALYs), and associated risk factors of IHD from the global burden of disease (GBD) 2021 study. Descriptive, decomposition, and risk factor analyses were used to provide insights into the epidemiologic patterns of IHD from 1990 to 2021 and project the burden of IHD from 2022 to 2045. Potential differences in burden and risk factors based on age, sex, 21 GBD geographic regions, five social development index (SDI) regions, and 204 countries are highlighted.
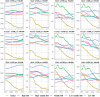
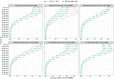
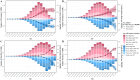
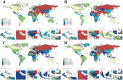
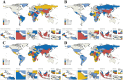
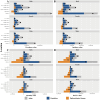
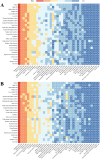
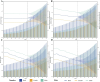
Results: Globally, the age-standardized prevalence rate (ASPR) of IHD is increasing, while the age-standardized incidence rate (ASIR), age-standardized mortality rate (ASMR), and age-standardized disability-adjusted life years (ASDR) are decreasing. ASPR, ASIR, ASMR, and ASDR were highest in the low-middle SDI regions and lowest in the high SDI regions. ASMR and ASDR were highest in Nauru and lowest in Portugal. Men had an overall heavier burden of IHD than women; the 65-69 age group had the largest burden, and those aged >95 years had the highest crude incidence rate. In addition, the burden of IHD was negatively correlated with SDI across regions and countries, while decomposition analyses suggest that the main reasons for the current increase in the burden of IHD are aging and population growth. Risk factors have changed relatively little over the 32 years, with metabolic risk still ranking first. We forecast that the absolute burden of IHD will continue to increase till 2045; however, ASIR, ASMR, and ASDR will gradually decline.
Conclusion: From 1990 to 2021, the global burden of IHD generally increased and varied across regions, sex, and age groups. Due to increasing population growth and aging, there is an urgent need for strategically directed measures to reduce the burden of IHD.
Keywords: decomposition analysis; forecast; global burden of disease; ischemic heart disease; risk factors.
Copyright © 2025 Cheng, Zhou, Zhong, Wang, Liu, Sun and Deng.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Trends and predictions of the global burden of ischemic heart disease in women of childbearing age attribute to high body mass index and hypertension,1990-2021: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study.BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2025 May 9;25(1):360. doi: 10.1186/s12872-025-04741-5. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2025. PMID: 40346517 Free PMC article.
-
Burden of uterine cancer in China from 1990 to 2021 and 15-year projection: a systematic analysis and comparison with global levels.Reprod Health. 2024 Oct 10;21(1):144. doi: 10.1186/s12978-024-01882-2. Reprod Health. 2024. PMID: 39390595 Free PMC article.
-
The global, regional, and national burden of paralytic ileus and intestinal obstruction, 1990 to 2021: a cross-sectional analysis from the 2021 global burden of disease study.Int J Surg. 2025 Feb 1;111(2):1773-1787. doi: 10.1097/JS9.0000000000002189. Int J Surg. 2025. PMID: 39784557
-
Global burden of motor neuron disease: unraveling socioeconomic disparities, aging dynamics, and divergent future trajectories (1990-2040).J Neurol. 2025 May 11;272(6):390. doi: 10.1007/s00415-025-13130-z. J Neurol. 2025. PMID: 40349275 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Global, regional and national burden of knee osteoarthritis 1990-2021: A systematic analysis of the Global Burden of Disease study 2021.Arch Gerontol Geriatr. 2025 Sep;136:105867. doi: 10.1016/j.archger.2025.105867. Epub 2025 May 9. Arch Gerontol Geriatr. 2025. PMID: 40403596 Review.
Cited by
-
New Perspectives in Cardiac and Vascular Diseases.Biomedicines. 2025 Jun 4;13(6):1377. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines13061377. Biomedicines. 2025. PMID: 40564096 Free PMC article.
References
-
- GBD 2021 Diseases and Injuries Collaborators . Global incidence, prevalence, years lived with disability (YLDs), disability-adjusted life-years (DALYs), and healthy life expectancy (HALE) for 371 diseases and injuries in 204 countries and territories and 811 subnational locations, 1990-2021: a systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2021. Lancet. (2024) 403:2133–61. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(24)00757-8 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Yusuf S, Joseph P, Rangarajan S, Islam S, Mente A, Hystad P, et al. . Modifiable risk factors, cardiovascular disease, and mortality in 155 722 individuals from 21 high-income, middle-income, and low-income countries (PURE): a prospective cohort study. Lancet. (2020) 395:795–808. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(19)32008-2, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

