Molecular characterization and immune role of TLR7 in Labeo rohita
- PMID: 40352938
- PMCID: PMC12062079
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1555048
Molecular characterization and immune role of TLR7 in Labeo rohita
Abstract
Background: Toll-like receptors (TLRs) play a vital role in the immune response by recognizing pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) and triggering signaling pathways that activate innate immunity. In bony fish, TLR7 is essential for both antiviral and antibacterial defense; however, its interactions with a wide range of ligands and pathogens are still not well understood across various fish species. This study focuses on the identification and characterization of TLR7 in Labeo rohita (LrTLR7) and aims to evaluate its response to pathogen challenges and stimulation by PAMPs.
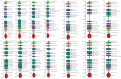
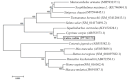
Methods: To clone the TLR7 gene, RNA was extracted from L. rohita kidney tissue using a standard protocol, followed by cDNA synthesis with commercial kits. The TLR7 gene was amplified by PCR, and the gel-purified product was cloned into the pGEM-T Easy vector. DNA sequencing and BLAST analysis confirmed the identity of the LrTLR7 gene. The ORF of LrTLR7 cDNA was predicted using ORF-finder, while structural motifs in the encoded protein were identified through SMART. Phylogenetic relationships were analyzed using MEGA7 to construct evolutionary trees. Gene expression profiles of LrTLR7 were evaluated by quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) across developmental stages, tissues/organs of rohu fingerlings, and during challenges with A, hydrophila and E. tarda infections, as well as LPS and Poly I:C stimulation. Mucosal RBCs and PBLs were isolated using density-gradient centrifugation with HiSep™ LSM 1077 (Himedia, India). Cultured L. rohita gill (LRG) cells in Leibovitz's L-15 medium were infected with A. hydrophila or E. tarda at a multiplicity of infection (MOI) of 1, following established protocols.
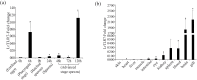
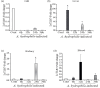
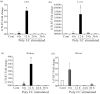
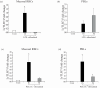
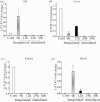
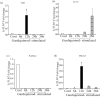
Results: LrTLR7 showed the closest phylogenetic affinity to TLR7 in Cyprinus carpio. During embryonic development, LrTLR7 expression surged dramatically (~111-fold, p<0.05) in embryos at 120 h post-fertilization (hpf). In L. rohita juveniles, the gene was ubiquitously expressed across tissues/organs, with peak expression in gills (~2,000-fold). Following infection with A. hydrophila or E tarda, LrTLR7 gene transcripts in the liver increased sharply at 6 hpi (~93-fold and ~53,000-fold, respectively). In the infected fish, mucosal RBCs showed a ~500,000-fold upregulation (p<0.05), while PBLs exhibited maximal responses at 24 hpi (~5,000-fold for A. hydrophila and ~10 million-fold for E. tarda). In the LRG cell line, LrTLR7 gene expression rose ~30-fold by 3 hpi. during A. hydrophila infection. In-vivo stimulation with LPS or poly I:C triggered a ~30,000-fold increase in hepatic LrTLR7 expression at 12 h post-stimulation, with kidney tissue showing secondary activation. Mucosal RBCs and PBLs displayed rapid (1-3 h) LrTLR7 upregulation following in-vitro ligand exposure. Imiquimod and gardiquimod activated LrTLR7-signalling pathways in both in-vivo and in-vitro systems, elevating transcription of IRF7 and type I interferon genes.
Conclusion: Similar to higher vertebrates, LrTLR7 plays a crucial role in responding to pathogenic invasions and various PAMPs to induce innate immunity. Consequently, TLR7 in fish represents a significant target for immune activation using specific agonists or ligands, which could aid in the prevention of fish diseases.
Keywords: Labeo rohita; PAMPS; PBLs; RBCs; TLR7; TLRs; Type-I IFN; innate immunity.
Copyright © 2025 Pani, Ganguly, Mahapatra, Dash, Das, Saha and Samanta.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures






References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

