ADL and Cognitive Function in Chinese Elderly: Mediating Role of Social Participation and Moderating Role of Intergenerational Support
- PMID: 40353048
- PMCID: PMC12065469
- DOI: 10.2147/JMDH.S523168
ADL and Cognitive Function in Chinese Elderly: Mediating Role of Social Participation and Moderating Role of Intergenerational Support
Abstract
Purpose: This study aimed to explore the relationship between activities of daily living (ADL) and cognitive function in Chinese elderly, and to analyze in depth the mediating and moderating roles of social participation and children's intergenerational support in this relationship, in order to provide a reference basis for delaying cognitive decline in the elderly.
Patients and methods: Based on data from the 2020 wave of China Health and Retirement Longitudinal Survey (CHARLS 2020), this study included 5612 subjects aged 60 years and older, and extracted main variables such as demographic information, ADL, social participation, cognitive function, and children's intergenerational support. Descriptive statistics and Pearson's correlation analysis in SPSS 27.0 were used to analyze the relationship between the main variables, and regression and Bootstrap analysis in SPSS 27.0 PROCESS macro (Model 4 and Model 14) were further used to analyze the mediating and moderating effects.
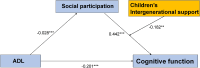
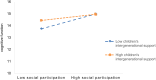
Results: Among Chinese elderly, ADL significantly positively correlated with social participation (r = 0.086, P < 0.001) and cognitive function (r = 0.193, P < 0.001), and social participation significantly positively correlated with cognitive function (r = 0.144, P < 0.001). Social participation partially mediated the relationship between ADL and cognitive function (β = -0.202, P < 0.001), accounting for 5.74% of the total effect. Moreover, children's intergenerational support negatively moderated the relationship between social participation and cognitive function (β = -0.182, P < 0.001). Thus, a moderated mediation model was developed.
Conclusion: ADL can affect cognitive function directly or indirectly through social participation in elderly. Furthermore, children's intergenerational support plays a negative moderating role in this mechanism. Therefore, governments, hospitals, communities, and families should provide personalized intervention strategies for elderly to delay cognitive decline and promote healthy aging through early prevention of ADL impairment, promotion of social participation, and optimization of family support.
Keywords: activities of daily living; cognitive function; elderly; intergenerational support; social participation.
© 2025 Li et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
References
-
- United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs. World Social Report 2023: Leaving No One Behind in an Ageing World. New York: United Nations; 2023.
-
- Rollnik-Sadowska E, Slavkovic M, Ana-Maria Bercu AM, et al. Public service motivation and job satisfaction: the role of social support during crisis. Equilib Q J Econ Econ Policy. 2023;18(4):1179–1215. doi: 10.24136/eq.2023.037 - DOI
-
- Slavkovic M, Sretenovic S, Bugarcic M. Remote working for sustainability of organization during the COVID-19 pandemic: the mediator-moderator role of social support. Sustainability. 2022;14(1). doi: 10.3390/su14010070 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources