Exploring the mechanisms of artemisinin and its derivatives in the treatment of atopic dermatitis based on network pharmacology and molecular docking: A review
- PMID: 40355181
- PMCID: PMC12074105
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000042287
Exploring the mechanisms of artemisinin and its derivatives in the treatment of atopic dermatitis based on network pharmacology and molecular docking: A review
Abstract
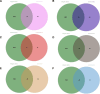
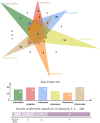
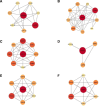
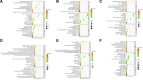
This study investigates the therapeutic mechanisms of artemisinin (ARS) and its derivatives in atopic dermatitis (AD) using network pharmacology and molecular docking. Molecules and disease targets were screened using public databases, including SwissTargetPrediction, PharmMapper, and Genecards. Core targets were identified, and a protein-protein interaction (PPI) network was constructed using STRING and Cytoscape for topological analysis. Relevant data were obtained from the DAVID database for Gene Ontology (GO) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) enrichment analysis. Molecular docking of ARS and its derivatives with target genes was performed using AutoDock, with results visualized in Pymol. A functional PPI network was established, and molecular docking demonstrated strong binding activity between ARS derivatives and target protein. Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase14 (MAPK14) and Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase10 (MAPK10) was found to be a common target for their treatment of AD. ARS and its derivatives may treat AD by modulating pathways such as Prolactin signaling, cancer pathways, neuroactive ligand-receptor interaction, and IL-17 signaling. ARS and its derivatives have the potential to treat AD. Artemisinin, artesunate, dihydroartemisinin, artemether, artemisinin and artemisinone could potentially treat AD by targeting MAPK14 and MAPK10.
Keywords: artemisinin; artesunate; dihydroartemisinin; molecular docking; network pharmacology.
Copyright © 2025 the Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no funding and conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
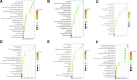
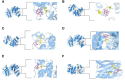
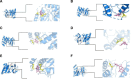
Similar articles
-
Exploring the Potential Mechanism of Artemisinin and Its Derivatives in the Treatment of Osteoporosis Based on Network Pharmacology and Molecular Docking.Comput Math Methods Med. 2022 Dec 22;2022:3976062. doi: 10.1155/2022/3976062. eCollection 2022. Comput Math Methods Med. 2022. PMID: 36590764 Free PMC article.
-
Network Pharmacology, Molecular Docking and Experimental Verification Revealing the Mechanism of Fule Cream against Childhood Atopic Dermatitis.Curr Comput Aided Drug Des. 2024;20(6):860-875. doi: 10.2174/0115734099257922230925074407. Curr Comput Aided Drug Des. 2024. PMID: 37807411
-
Exploring the mechanisms underlying the therapeutic effect of Salvia miltiorrhiza in diabetic nephropathy using network pharmacology and molecular docking.Biosci Rep. 2021 Jun 25;41(6):BSR20203520. doi: 10.1042/BSR20203520. Biosci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33634308 Free PMC article.
-
Integration of Network Pharmacology and Molecular Docking Technology Reveals the Mechanism of the Therapeutic Effect of Xixin Decoction on Alzheimer's Disease.Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2022;25(10):1785-1804. doi: 10.2174/1386207325666220523151119. Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2022. PMID: 35616676
-
Exploring the mechanism of action of Yiyi Fuzi Baijiang powder in colorectal cancer based on network pharmacology and molecular docking studies.Biotechnol Genet Eng Rev. 2023 Oct;39(2):1107-1127. doi: 10.1080/02648725.2023.2167765. Epub 2023 Feb 3. Biotechnol Genet Eng Rev. 2023. PMID: 36735641 Review.
References
-
- Katoh N, Ohya Y, Ikeda M, et al. ; Committee for Clinical Practice Guidelines for the Management of Atopic Dermatitis 2018, The Japanese Society of Allergology, The Japanese Dermatology Association. Japanese guidelines for atopic dermatitis 2020. Allergol Int. 2020;69:356–69. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

