Susceptibility from the immunological perspective of COVID-19-associated pulmonary aspergillosis: A literature review
- PMID: 40355215
- PMCID: PMC12073940
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000042363
Susceptibility from the immunological perspective of COVID-19-associated pulmonary aspergillosis: A literature review
Abstract
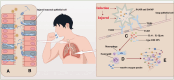
The incidence rate of COVID-19-associated pulmonary aspergillosis (CAPA) is rising. However, the pathogenesis of CAPA remains unclear. Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection disrupts pathways related to type I interferon and Toll-like receptors, key components in innate immunity, thereby elevating the incidence of CAPA. Additionally, SARS-CoV-2 infection results in T and B cell functional deficiencies or exhaustion within adaptive immunity, weakening the defense against invasive Aspergillus. Furthermore, SARS-CoV-2 infection enhances the replication of cytomegalovirus and alters the gut microbiota, factors that may aid in diagnosing CAPA. Immunosuppressive therapy in COVID-19 patients is also believed to heighten the risk of invasive aspergillosis. Therefore, this review, examines the immune response to SARS-CoV-2 infection combined with invasive aspergillosis, and explores the pathogenesis and susceptibility factors of CAPA. We propose that variations in an individual's immune response significantly determine susceptibility to CAPA. The aim of this paper is to deepen clinical understanding of CAPA's pathogenesis, thereby aiding in mitigating susceptibility risk and advancing novel treatment approaches.
Keywords: CAPA; COVID-19 drug treatment; COVID-19-associated pulmonary aspergillosis; SARS-CoV-2; immuneresponse.
Copyright © 2025 the Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures

References
-
- Sushma DS, Jaiswal V, Kumar A, Asha S, Pal T. Insights into Novel Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19): current understanding, research, and therapeutic updates. Recent Pat Biotechnol. 2022;16:35–63. - PubMed
-
- Paredes MI, Lunn SM, Famulare M, et al. . Associations between severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) variants and risk of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) hospitalization among confirmed cases in Washington State: a retrospective cohort study. Clin Infect Dis. 2022;75:e536–44. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

