Evaluating the cost-effectiveness of replacing lansoprazole with vonoprazan for treating erosive oesophagitis
- PMID: 40355277
- PMCID: PMC12083356
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjgast-2024-001709
Evaluating the cost-effectiveness of replacing lansoprazole with vonoprazan for treating erosive oesophagitis
Abstract
Objective: This cost-effectiveness analysis compares vonoprazan against lansoprazole, a gold-standard proton pump inhibitor, in managing erosive oesophagitis.
Methods: The economic evaluation was carried out using data from a double-blind, randomised control trial. Costs were measured in pounds sterling. Effectiveness was assessed on a binary scale, resolution versus non-resolution of disease, after 32 weeks.
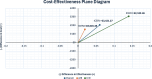
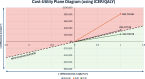
Results: The primary analysis produced an incremental cost-effectiveness ratio (ICER) of £3421.27 per resolution. After applying quality-adjusted life year (QALY) data from the REFLUX trial (2008), we derived an ICER/QALY of £34 747.32, marginally exceeding the £30 000 threshold set by the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. However, further subgroup analysis showed cost-effectiveness when healing severe grades of oesophagitis (ICER/QALY of £22 165.56). The first sensitivity analysis considers the typically non-invasive determination of disease resolution; the ICER/QALY of £15 826.98 supports vonoprazan's use in treating severe oesophagitis. The second considers a longer healing phase alongside a stronger 30 mg maintenance dose of lansoprazole, concordant with current guidelines; the ICER/QALY of £43 998.39 suggests the guidelines (regarding dosage, frequency and duration) must be optimised for vonoprazan. The final sensitivity analysis accounts for variations in quality-of-life measures, which grossly inflate the ICER/QALY (£118 216.32); this emphasises that vonoprazan should mainly be considered for patients with persistent symptoms and high severity.
Conclusion: Vonoprazan is potentially cost-effective for the initial healing of severe oesophagitis, after endoscopic diagnosis. Further trials and economic evaluations are necessary for the symptom-based prescription of vonoprazan and to determine the optimal dosage, frequency and duration.
Keywords: COST-EFFECTIVENESS; ECONOMIC EVALUATION; GASTROESOPHAGEAL REFLUX DISEASE; HEALTH ECONOMICS; PROTON PUMP INHIBITION.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2025. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ Group.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Phase III, randomised, double-blind, multicentre study to evaluate the efficacy and safety of vonoprazan compared with lansoprazole in Asian patients with erosive oesophagitis.Gut. 2020 Feb;69(2):224-230. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2019-318365. Epub 2019 Aug 13. Gut. 2020. PMID: 31409606 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Cost-Utility Analysis of CYP2C19 Genotype Detection for Selection of Acid-Suppressive Therapy with Lansoprazole or Vonoprazan for Patients with Reflux Esophagitis in China.Clin Drug Investig. 2022 Oct;42(10):839-851. doi: 10.1007/s40261-022-01188-w. Epub 2022 Aug 22. Clin Drug Investig. 2022. PMID: 35994227
-
Randomised clinical trial: vonoprazan, a novel potassium-competitive acid blocker, vs. lansoprazole for the healing of erosive oesophagitis.Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2016 Jan;43(2):240-51. doi: 10.1111/apt.13461. Epub 2015 Nov 11. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2016. PMID: 26559637 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Vonoprazan is superior to lansoprazole for healing of severe but not mild erosive esophagitis: A systematic review with meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024 Jun;39(6):988-999. doi: 10.1111/jgh.16486. Epub 2024 Feb 14. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024. PMID: 38353152
-
Vonoprazan versus proton-pump inhibitors for healing gastroesophageal reflux disease: A systematic review.J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019 Aug;34(8):1316-1328. doi: 10.1111/jgh.14664. Epub 2019 Apr 11. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019. PMID: 30883868
References
-
- BMJ Best Practice Homepage. 2023. [10-Mar-2025]. https://bestpractice.bmj.com/info/ Available. Accessed.
-
- NICE Recommendations | Gastro-oesophageal reflux disease and dyspepsia in adults: investigation and management | Guidance. 2014. [10-Mar-2025]. https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/cg184/chapter/Recommendations Available. Accessed. - PubMed
-
- Endoscopy Campus Reflux esophagitis: Los Angeles classification. 2025. [10-Mar-2025]. https://www.endoscopy-campus.com/en/classifications/reflux-esophagitis-l... Available. Accessed.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
