Assessment of male partner involvement in triple ART drug adherence and associated factors among HIV-positive pregnant women in government hospitals of the North Gojjam Zone, Amhara Region, Northwest Ethiopia, 2023: a multicentre cross-sectional study
- PMID: 40355295
- PMCID: PMC12083407
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2024-096713
Assessment of male partner involvement in triple ART drug adherence and associated factors among HIV-positive pregnant women in government hospitals of the North Gojjam Zone, Amhara Region, Northwest Ethiopia, 2023: a multicentre cross-sectional study
Abstract
Background: The involvement of male partners in the care and treatment of HIV-positive pregnant women is essential for improving health outcomes and ensuring optimal adherence to antiretroviral therapy (ART). Although ART has been shown to be effective in preventing mother-to-child transmission of HIV, maintaining adherence to the prescribed triple ART regimen remains a significant challenge. However, there has been a lack of research on the role of male partners in supporting ART adherence during pregnancy.
Objective: To assess male partner involvement in triple ART drug adherence and associated factors among HIV-positive pregnant women in government hospitals of the North Gojjam Zone, Amhara Region, Northwest Ethiopia, 2023.
Design: An institution-based cross-sectional study was conducted.
Setting: The study was carried out in hospitals located in the North Gojjam Zone of Northwest Ethiopia.
Participants: The study was conducted among 410 male partners of HIV-positive pregnant women from 1 April 2023 to 30 May 2023.
Primary and secondary outcomes: The primary outcome was to assess the involvement of male partners in triple ART adherence, while the secondary outcome was to identify factors associated with the involvement of male partners on triple ART adherence among HIV-positive pregnant women. The association between variables was assessed using bivariate and multivariable logistic regression models, and a p value <0.05 with a 95% CI was considered statistically significant.
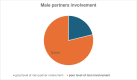
Results: A total of 410 participants were included, with a response rate of 97.2%. The prevalence of male partner involvement in triple ART drug adherence among HIV-positive pregnant women was 21.2%. Multivariable logistic regression showed that educational status (AOR (Adjusted Odds Ratio)=2.5, 95% CI 1.26 to 4.96), place of residence (AOR=4.8, 95% CI 3.17 to 7.27), and the time taken to travel from home to the facility (AOR=3.1, 95% CI 1.51 to 6.36) were significantly associated with male partner involvement.
Conclusion: This study demonstrates that compared with a study conducted in Malawi, male partner involvement in triple ART drug adherence was lower. Male partner involvement in triple ART adherence among HIV-positive pregnant women was strongly associated with educational status, place of residence and the time taken to travel from home to the health facility. Empowering men to actively participate in healthcare decisions and treatment plans for their partners can foster a sense of responsibility and enhance commitment to adherence.
Keywords: Chronic Disease; Health; INFECTIOUS DISEASES; Midwifery; Pregnancy; Public health.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2025. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ Group.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Level of option B+PMTCT drug adherence with male partner involvement and associated factors among breastfeeding women until 18 months in North Gojjam Zone, Amhara region, Northwest Ethiopia, 2022: a multicentre cross-sectional study.BMJ Open. 2024 Oct 22;14(10):e086374. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2024-086374. BMJ Open. 2024. PMID: 39438089 Free PMC article.
-
Option B plus antiretroviral therapy adherence and associated factors among HIV positive pregnant women in Southern Ethiopia.BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2019 Feb 28;19(1):82. doi: 10.1186/s12884-019-2228-4. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2019. PMID: 30819147 Free PMC article.
-
Levels of option B+ ART drugs adherence and associated factors among pregnant women following ART services at public health facilities of East Shawa Zone, Oromia, Ethiopia.Sex Reprod Healthc. 2019 Dec;22:100459. doi: 10.1016/j.srhc.2019.100459. Epub 2019 Aug 13. Sex Reprod Healthc. 2019. PMID: 31442747
-
Medication adherence in pregnant women with human immunodeficiency virus receiving antiretroviral therapy in sub-Saharan Africa: a systematic review.BMC Public Health. 2018 Jun 27;18(1):805. doi: 10.1186/s12889-018-5651-y. BMC Public Health. 2018. PMID: 29945601 Free PMC article.
-
Magnitude and risk factors of mother-to-child transmission of HIV among HIV-exposed infants after Option B+ implementation in Ethiopia: a systematic review and meta-analysis.AIDS Res Ther. 2024 Jun 7;21(1):39. doi: 10.1186/s12981-024-00623-6. AIDS Res Ther. 2024. PMID: 38849895 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Boateng D, Kwapong GD, Agyei-Baffour P. Knowledge, perception about antiretroviral therapy (ART) and prevention of mother-to-child-transmission (PMTCT) and adherence to ART among HIV positive women in the Ashanti Region, Ghana: a cross-sectional study. BMC Womens Health . 2013;13:2. doi: 10.1186/1472-6874-13-2. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Carter MW. “Because he loves me”: Husbands’ involvement in maternal health in Guatemala. Cult Health Sex. 2002;4:259–79. doi: 10.1080/13691050110112784. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous