Application of interpretable machine learning algorithms to predict macroangiopathy risk in Chinese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
- PMID: 40355529
- PMCID: PMC12069545
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-01161-5
Application of interpretable machine learning algorithms to predict macroangiopathy risk in Chinese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Abstract
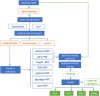
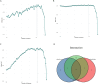
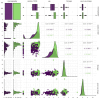
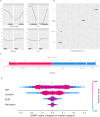
Macrovascular complications are leading causes of morbidity and mortality in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), yet early diagnosis of cardiovascular disease (CVD) in this population remains clinically challenging. This study aims to develop a machine learning model that can accurately predict diabetic macroangiopathy in Chinese patients. A retrospective cross-sectional analytical study was conducted on 1566 hospitalized patients with T2DM. Feature selection was performed using recursive feature elimination (RFE) within the mlr3 framework. Model performance was benchmarked using 29 machine learning (ML) models, with the ranger model selected for its superior performance. Hyperparameters were optimized through grid search and 5-fold cross-validation. Model interpretability was enhanced using SHAP values and PDPs. An external validation set of 106 patients was used to test the model. Key predictive variables identified included the duration of T2DM, age, fibrinogen, and serum urea nitrogen. The predictive model for macroangiopathy was established and showed good discrimination performance with an accuracy of 0.716 and an AUC of 0.777 in the training set. Validation on the external dataset confirmed its robustness with an AUC of 0.745. This study establish an approach based on machine learning algorithm in features selection and the development of prediction tools for diabetic macroangiopathy.
Keywords: Machine learning methods; Macroangiopathy; Prediction model; Risk factor; T2DM.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests. Ethics approval and consent to participate: This study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of the First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University. Written informed consent to participate was obtained from all participants.
Figures

References
-
- Bahardoust, M. et al. Effect of Metformin (vs. Placebo or sulfonylurea) on all-cause and cardiovascular mortality and incident cardiovascular events in patients with diabetes: an umbrella review of systematic reviews with meta-analysis. J. Diabetes Metab. Disord. 23 (1), 27–38 (2023). - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
- 82102281/the National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 2021JJ40867/the Natural Scientific Foundation of Hunan Province
- 2021JJ40893/the Natural Scientific Foundation of Hunan Province
- 202101062143/the Scientific Research Fund of Hunan Province Health Commission
- 202101062143/the Scientific Research Fund of Hunan Province Health Commission
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

