The microprotein C16orf74/MICT1 promotes thermogenesis in brown adipose tissue
- PMID: 40355556
- PMCID: PMC12170882
- DOI: 10.1038/s44318-025-00444-x
The microprotein C16orf74/MICT1 promotes thermogenesis in brown adipose tissue
Abstract
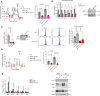
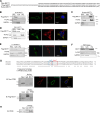
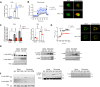
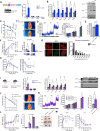
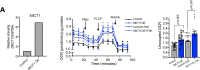
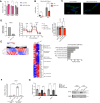
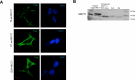
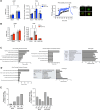
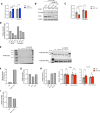
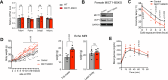
Brown and beige adipose tissues are metabolically beneficial for increasing energy expenditure via thermogenesis, mainly through UCP1 (uncoupling protein 1). Here, we identify C16orf74, subsequently named MICT1 (microprotein for thermogenesis 1), as a microprotein that is specifically and highly expressed in brown adipose tissue (BAT) and is induced upon cold exposure. MICT1 interacts with protein phosphatase 2B (PP2B, calcineurin) through the docking motif PNIIIT, thereby interfering with dephosphorylation of the regulatory subunit of protein kinase A (PKA), RIIβ, and potentiating PKA activity in brown adipocytes. Overexpression of MICT1 in differentiated brown adipocytes promotes thermogenesis, showing increased oxygen consumption rate (OCR) with higher thermogenic gene expression during β3-adrenergic stimulation, while knockdown of MICT1 impairs thermogenic responses. Moreover, BAT-specific MICT1 ablation in mice suppresses thermogenic capacity to increase adiposity and insulin resistance. Conversely, MICT1 overexpression in BAT or treating mice with a chemical inhibitor that targets the PP2B docking motif of MICT1 enhances thermogenesis. This results in cold tolerance and increased energy expenditure, protection against diet-induced and genetic obesity and insulin resistance, thus suggesting a therapeutic potential of MICT1 targeting.
Keywords: Brown Adipose Tissue (Thermogenesis); C16orf74 (MICT1); Microprotein; PP2B (Calcineurin); Protein Kinase A (PKA).
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure and competing interests statement. The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




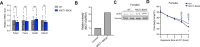
Similar articles
-
S100A8/S100A9 impairs energy expenditure and whole body metabolism.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2025 Aug 1;329(2):E341-E354. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00076.2025. Epub 2025 Jul 15. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2025. PMID: 40662569
-
Mitochondrial ATP-sensitive K+ channels (MitoKATP) regulate brown adipocyte differentiation and metabolism.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2025 Aug 1;329(2):C574-C584. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00070.2025. Epub 2025 Jul 11. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2025. PMID: 40643190
-
Ablation of FAM210A in Brown Adipocytes of Mice Exacerbates High-Fat Diet-Induced Metabolic Dysfunction.Diabetes. 2025 Mar 1;74(3):282-294. doi: 10.2337/db24-0294. Diabetes. 2025. PMID: 39602358
-
Adipose tissue browning and thermogenesis under physiologically energetic challenges: a remodelled thermogenic system.J Physiol. 2024 Jan;602(1):23-48. doi: 10.1113/JP285269. Epub 2023 Nov 29. J Physiol. 2024. PMID: 38019069 Review.
-
Brown and beige adipose tissue-derived metabokine and lipokine inter-organ signalling in health and disease.Exp Physiol. 2025 Jul;110(7):918-935. doi: 10.1113/EP092008. Epub 2024 Nov 26. Exp Physiol. 2025. PMID: 39591977 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Multiomics Integration of Parkinson's Disease Datasets Reveals Unexpected Roles of IRE1 in Its Pathology.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jul 12;26(14):6711. doi: 10.3390/ijms26146711. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40724959 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Blumenthal DK, Takio K, Hansen RS, Krebs EG (1986) Dephosphorylation of cAMP-dependent protein kinase regulatory subunit (type II) by calmodulin-dependent protein phosphatase. Determinants of substrate specificity. J Biol Chem 261(18):8140–8145 - PubMed
-
- Bock A, Annibale P, Konrad C, Hannawacker A, Anton SE, Maiellaro I, Zabel U, Sivaramakrishnan S, Falcke M, Lohse MJ (2021) Optical mapping of cAMP signaling at the nanometer scale. Cell 184(10):2793 - PubMed
-
- Bradburn DA, Reis JC, Qayyum S, Viennet T, Arthanari H, Cyert MS (2004) A novel motif in calcimembrin/C16orf74 dictates multimeric dephosphorylation by calcineurin. Preprint at 10.1101/2024.05.12.593783
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

