Gut microbiota-dependent increase in phenylacetic acid induces endothelial cell senescence during aging
- PMID: 40355758
- PMCID: PMC12176623
- DOI: 10.1038/s43587-025-00864-8
Gut microbiota-dependent increase in phenylacetic acid induces endothelial cell senescence during aging
Abstract
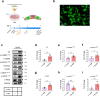
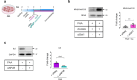
Endothelial cell senescence is a key driver of cardiovascular aging, yet little is known about the mechanisms by which it is induced in vivo. Here we show that the gut bacterial metabolite phenylacetic acid (PAA) and its byproduct, phenylacetylglutamine (PAGln), are elevated in aged humans and mice. Metagenomic analyses reveal an age-related increase in PAA-producing microbial pathways, positively linked to the bacterium Clostridium sp. ASF356 (Clos). We demonstrate that colonization of young mice with Clos increases blood PAA levels and induces endothelial senescence and angiogenic incompetence. Mechanistically, we find that PAA triggers senescence through mitochondrial H2O2 production, exacerbating the senescence-associated secretory phenotype. By contrast, we demonstrate that fecal acetate levels are reduced with age, compromising its function as a Sirt1-dependent senomorphic, regulating proinflammatory secretion and redox homeostasis. These findings define PAA as a mediator of gut-vascular crosstalk in aging and identify sodium acetate as a potential microbiome-based senotherapy to promote healthy aging.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
















References
-
- Saeedi Saravi, S. S. & Feinberg, M. W. Can removal of zombie cells revitalize the aging cardiovascular system? Eur. Heart J.45, 867–869 (2024). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- #21A053/Novartis Stiftung für Medizinisch-Biologische Forschung (Novartis Foundation for Medical-Biological Research)
- #310030_21A053/Schweizerischer Nationalfonds zur Förderung der Wissenschaftlichen Forschung (Swiss National Science Foundation)
- #CRSK-3_229134/Schweizerischer Nationalfonds zur Förderung der Wissenschaftlichen Forschung (Swiss National Science Foundation)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

