Decoding innate lymphoid cells and innate-like lymphocytes in asthma: pathways to mechanisms and therapies
- PMID: 40355861
- PMCID: PMC12067961
- DOI: 10.1186/s12929-025-01142-w
Decoding innate lymphoid cells and innate-like lymphocytes in asthma: pathways to mechanisms and therapies
Abstract
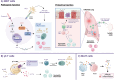
Asthma is a chronic inflammatory lung disease driven by a complex interplay between innate and adaptive immune components. Among these, innate lymphoid cells (ILCs) and innate-like lymphocytes have emerged as crucial players in shaping the disease phenotype. Within the ILC family, group 2 ILCs (ILC2s), in particular, contribute significantly to type 2 inflammation through their rapid production of cytokines such as IL-5 and IL-13, promoting airway eosinophilia and airway hyperreactivity. On the other hand, innate-like lymphocytes such as invariant natural killer T (iNKT) cells can play either pathogenic or protective roles in asthma, depending on the stimuli and lung microenvironment. Regulatory mechanisms, including cytokine signaling, metabolic and dietary cues, and interactions with other immune cells, play critical roles in modulating their functions. In this review, we highlight current findings on the role of ILCs and innate-like lymphocytes in asthma development and pathogenesis. We also examine the underlying mechanisms regulating their function and their interplay with other immune cells. Finally, we explore current therapies targeting these cells and their effector cytokines for asthma management.
Keywords: Asthma; ILCs; Immune regulation; Innate-like lymphocytes; Therapeutic targets.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Innate lymphoid cells contribute to allergic airway disease exacerbation by obesity.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2016 Nov;138(5):1309-1318.e11. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2016.03.019. Epub 2016 Apr 4. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2016. PMID: 27177781
-
Innate lymphoid cells in asthma: Will they take your breath away?Eur J Immunol. 2016 Apr;46(4):795-806. doi: 10.1002/eji.201444557. Epub 2016 Mar 16. Eur J Immunol. 2016. PMID: 26891006 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Group 2 innate lymphoid cells and CD4+ T cells cooperate to mediate type 2 immune response in mice.Allergy. 2014 Oct;69(10):1300-7. doi: 10.1111/all.12446. Epub 2014 Jun 17. Allergy. 2014. PMID: 24939388 Free PMC article.
-
Innate immunity in the lung regulates the development of asthma.Immunol Rev. 2014 Jul;260(1):235-48. doi: 10.1111/imr.12187. Immunol Rev. 2014. PMID: 24942693 Review.
-
Innate immune crosstalk in asthmatic airways: Innate lymphoid cells coordinate polarization of lung macrophages.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2019 May;143(5):1769-1782.e11. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2018.10.040. Epub 2018 Nov 9. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2019. PMID: 30414858
References
-
- Lang DM. Severe asthma: epidemiology, burden of illness, and heterogeneity. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2015;36(6):418–24. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

