Identification of HER2-over-expression, HER2-low-expression, and HER2-zero-expression statuses in breast cancer based on 18F-FDG PET/CT radiomics
- PMID: 40355910
- PMCID: PMC12070556
- DOI: 10.1186/s40644-025-00880-2
Identification of HER2-over-expression, HER2-low-expression, and HER2-zero-expression statuses in breast cancer based on 18F-FDG PET/CT radiomics
Abstract
Purpose: According to the updated classification system, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) expression statuses are divided into the following three groups: HER2-over-expression, HER2-low-expression, and HER2-zero-expression. HER2-negative expression was reclassified into HER2-low-expression and HER2-zero-expression. This study aimed to identify three different HER2 expression statuses for breast cancer (BC) patients using PET/CT radiomics and clinicopathological characteristics.
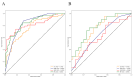
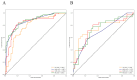
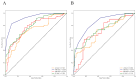
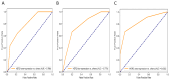
Methods and materials: A total of 315 BC patients who met the inclusion and exclusion criteria from two institutions were retrospectively included. The patients in institution 1 were divided into the training set and the independent validation set according to the ratio of 7:3, and institution 2 was used as the external validation set. According to the results of pathological examination, all BC patients were divided into HER2-over-expression, HER2-low-expression, and HER2-zero-expression. First, PET/CT radiomic features and clinicopathological features based on each patient were extracted and collected. Second, multiple methods were used to perform feature screening and feature selection. Then, four machine learning classifiers, including logistic regression (LR), k-nearest neighbor (KNN), support vector machine (SVM), and random forest (RF), were constructed to identify HER2-over-expression vs. others, HER2-low-expression vs. others, and HER2-zero-expression vs. others. The receiver operator characteristic (ROC) curve was plotted to measure the model's predictive power.
Results: According to the feature screening process, 8, 10, and 2 radiomics features and 2 clinicopathological features were finally selected to construct three prediction models (HER2-over-expression vs. others, HER2-low-expression vs. others, and HER2-zero-expression vs. others). For HER2-over-expression vs. others, the RF model outperformed other models with an AUC value of 0.843 (95%CI: 0.774-0.897), 0.785 (95%CI: 0.665-0.877), and 0.788 (95%CI: 0.708-0.868) in the training set, independent validation set, and external validation set. Concerning HER2-low-expression vs. others, the outperformance of the LR model over other models was identified with an AUC value of 0.783 (95%CI: 0.708-0.846), 0.756 (95%CI: 0.634-0.854), and 0.779 (95%CI: 0.698-0.860) in the training set, independent validation set, and external validation set. Whereas, the KNN model was confirmed as the optimal model to distinguish HER2-zero-expression from others, with an AUC value of 0.929 (95%CI: 0.890-0.958), 0.847 (95%CI: 0.764-0.910), and 0.835 (95%CI: 0.762-0.908) in the training set, independent validation set, and external validation set.
Conclusion: Combined PET/CT radiomic models integrating with clinicopathological characteristics are non-invasively predictive of different HER2 statuses of BC patients.
Keywords: Breast cancer; HER2; PET/CT; Radiomics.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethical approval and consent to participate: Our retrospective study was authorized by the Institutional Ethics Committee, which consented to waive informed consent because the data used in this study has no personally identifiable information of patients. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Discrimination between HER2-overexpressing, -low-expressing, and -zero-expressing statuses in breast cancer using multiparametric MRI-based radiomics.Eur Radiol. 2024 Sep;34(9):6132-6144. doi: 10.1007/s00330-024-10641-7. Epub 2024 Feb 16. Eur Radiol. 2024. PMID: 38363315
-
Intratumoral and peritumoral radiomics for preoperative prediction of neoadjuvant chemotherapy effect in breast cancer based on 18F-FDG PET/CT.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2024 Nov 2;150(11):484. doi: 10.1007/s00432-024-05987-w. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39488636 Free PMC article.
-
Can we skip invasive biopsy of sentinel lymph nodes? A preliminary investigation to predict sentinel lymph node status using PET/CT-based radiomics.BMC Cancer. 2024 Oct 25;24(1):1316. doi: 10.1186/s12885-024-13031-w. BMC Cancer. 2024. PMID: 39455907 Free PMC article.
-
Predictive value of radiomic signature based on 2-[18F]FDG PET/CT in HER2 status determination for primary breast cancer with equivocal IHC results.Eur J Radiol. 2023 Oct;167:111050. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2023.111050. Epub 2023 Aug 16. Eur J Radiol. 2023. PMID: 37598640
-
Preliminary study on the ability of the machine learning models based on 18F-FDG PET/CT to differentiate between mass-forming pancreatic lymphoma and pancreatic carcinoma.Eur J Radiol. 2024 Jul;176:111531. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2024.111531. Epub 2024 May 25. Eur J Radiol. 2024. PMID: 38820949
References
-
- Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68:394–424. - PubMed
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Wagle NS, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2023. CA Cancer J Clin. 2023;73:17–48. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

