Mass spectrometry-based metabolomic as a powerful tool to unravel the component and mechanism in TCM
- PMID: 40355943
- PMCID: PMC12067679
- DOI: 10.1186/s13020-025-01112-2
Mass spectrometry-based metabolomic as a powerful tool to unravel the component and mechanism in TCM
Abstract
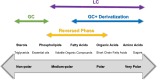
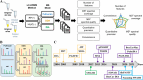
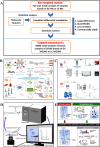
Mass spectrometry (MS)-based metabolomics has emerged as a transformative tool to unraveling components and their mechanisms in traditional Chinese medicine (TCM). The integration of advanced analytical platforms, such as LC-MS and GC-MS, coupled with metabolomics, has propelled the qualitative and quantitative characterization of TCM's complex components. This review comprehensively examines the applications of MS-based metabolomics in elucidating TCM efficacy, spanning chemical composition analysis, molecular target identification, mechanism-of-action studies, and syndrome differentiation. Recent innovations in functional metabolomics, spatial metabolomics, single-cell metabolomics, and metabolic flux analysis have further expanded TCM research horizons. Artificial intelligence (AI) and bioinformatics integration offer promising avenues for overcoming analytical bottlenecks, enhancing database standardization, and driving interdisciplinary breakthroughs. However, challenges remain, including the need for improved data processing standardization, database expansion, and understanding of metabolite-gene-protein interactions. By addressing these gaps, metabolomics can bridge traditional practices and modern biomedical research, fostering global acceptance of TCM. This review highlights the synergy of advanced MS techniques, computational tools, and TCM's holistic philosophy, presenting a forward-looking perspective on its clinical translation and internationalization.
Keywords: Component analysis; Mass spectrometry; Mechanism; Metabolomics; Traditional Chinese medicine.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: The manuscript is approved by all authors for publication. Competing interests: The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures



References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

