Vancomycin Treatment for Pneumobilia in Clostridioides difficile Infection: A Case Analysis
- PMID: 40356223
- PMCID: PMC12085102
- DOI: 10.12659/AJCR.947628
Vancomycin Treatment for Pneumobilia in Clostridioides difficile Infection: A Case Analysis
Abstract
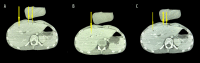
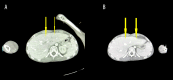
BACKGROUND Pneumobilia is the presence of air within the biliary tree. It is a relatively rare condition, usually caused by an abnormal communication between the biliary system and the gastrointestinal tract, or by infection from gas-forming bacteria. Antibiotic agents such as fluoroquinolones have many adverse effects, including Clostridioides difficile infection manifesting as colitis. Metronidazole has been used in the past and vancomycin and fidaxomicin can have good therapeutic results. CASE REPORT A 20-year-old man presented to Gennimatas General Hospital in Athens, Greece due to multiple episodes of diarrhea. He had received a 7-day treatment of oral levofloxacin, a common antibiotic treatment often used to treat Clostridioides difficile infection, until 10 days before presentation to our hospital as an outpatient treatment for mild pneumonia. Blood test revealed neutropenia and thrombocytopenia, and biochemical tests revealed hypokalemia and elevated inflammation markers. A CT scan of the abdomen showed pneumobilia. Blood and urine cultures were sterile, whereas Clostridioides difficile toxins A+ and B+ were detected in stool culture. Treatment with oral vancomycin had excellent results. The patient improved clinically and remained afebrile, with cessation of diarrhea, correction of electrolytic disorders, and disappearance of pneumobilia on a repeat CT scan after 1 week. CONCLUSIONS Pneumobilia caused by Clostridioides difficile infection was effectively treated with orally administered vancomycin, which cured our patient's diarrhea and pneumobilia.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Clostridioides difficile associated peritonitis in peritoneal dialysis patients - a case series based review of an under-recognized entity with therapeutic challenges.BMC Nephrol. 2020 Mar 4;21(1):76. doi: 10.1186/s12882-020-01734-8. BMC Nephrol. 2020. PMID: 32131755 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of Oral Metronidazole, Vancomycin, and Fidaxomicin on Host Shedding and Environmental Contamination With Clostridioides difficile.Clin Infect Dis. 2022 Mar 1;74(4):648-656. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciab473. Clin Infect Dis. 2022. PMID: 34017999 Clinical Trial.
-
[Updated Czech guidelines for the treatment of patients with colitis due to Clostridioides difficile].Klin Mikrobiol Infekc Lek. 2022 Sep;28(3):77-94. Klin Mikrobiol Infekc Lek. 2022. PMID: 36791303 Czech.
-
Primary clostridium difficile infection in patients with ulcerative colitis: Case report and literature review.Medicine (Baltimore). 2024 Feb 9;103(6):e36693. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000036693. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024. PMID: 38335423 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clostridium difficile appendicitis in an immunocompromised patient: a case report and review of the literature.J Med Case Rep. 2021 Jan 5;15(1):2. doi: 10.1186/s13256-020-02592-6. J Med Case Rep. 2021. PMID: 33402156 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous