The Nexus of HIV, substance abuse, and mental health among adolescents in Zambia (2021-2023)
- PMID: 40356736
- PMCID: PMC12067541
- DOI: 10.4102/jphia.v16i1.1229
The Nexus of HIV, substance abuse, and mental health among adolescents in Zambia (2021-2023)
Abstract
Background: Adolescents in Zambia face interrelated health challenges, including human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), substance abuse and mental health disorders (MHDs). These issues have significant public health implications, as substance abuse and MHDs are known to increase the risk of HIV incidence.
Aim: This study aimed to analyse trends in HIV incidence, substance abuse and MHDs among Zambian adolescents aged 10-19 years from 2021 to 2023.
Setting: Data were retrieved from the Health Management Information System under Zambia's Ministry of Health, covering all 10 provinces.
Methods: A retrospective analysis of secondary data was conducted using District Health Information Software 2 (DHIS2), the Ministry of Health's primary data system. Microsoft Excel and Stata were used for descriptive statistics and regression analysis to examine potential associations.
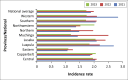
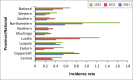
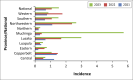
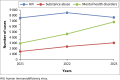
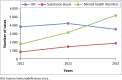
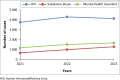
Results: Findings indicate an increase in national HIV incidence rates from 1.89 in 2021 to 1.99 in 2022, before a decrease to 1.73 in 2023. Substance abuse also showed an upward trend, rising from 0.35 to 0.68 per 1000 adolescents. Incidence of MHDs more than doubled from 0.7 in 2021 to 1.54 in 2023, with Lusaka and Northwestern provinces showing the most significant increases. Our linear correlational analysis showed a positive relationship among the key variables.
Conclusion: The results underscore the interconnectedness of HIV, substance abuse and mental health issues among adolescents in Zambia, emphasising the need for integrated interventions.
Contribution: This study contributes valuable insights for policy and programme development, highlighting the need for targeted, holistic approaches in adolescent health services to address these interconnected issues effectively.
Keywords: HIV; adolescents; incidence; mental health; substance abuse; trends.
© 2025. The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors reported that they received funding from Clinton Health Access Initiative. The authors have disclosed those interests fully and have implemented an approved plan for managing any potential conflicts arising from their involvement. The terms of these funding arrangements have been reviewed and approved by the affiliated university in accordance with its policy on objectivity in research.
Figures
References
-
- UNICEF DATA . Adolescent HIV prevention [homepage on the Internet]. [cited 2024 Aug 01]. Available from: https://data.unicef.org/topic/hivaids/adolescents-young-people/
-
- UNICEF Zambia . Evidence synthesis on adolescents health and HIV in Zambia [homepage on the Internet]. 2023. [cited 2024 Nov 07]. Available from: https://www.unicef.org/zambia/reports/evidence-synthesis-adolescents-hea...
-
- CDC - National Center for Health Statistics . Substance use – Health, United States [homepage on the Internet]. 2024. [cited 2024 Nov 06]. Available from: https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/hus/sources-definitions/substance-use.htm
-
- World Health Organization . Over 3 million annual deaths because of alcohol and drug use, majority among men [homepage on the Internet]. [cited 2024 Nov 06]. Available from: https://www.who.int/news/item/25-06-2024-over-3-million-annual-deaths-du...
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
