A report of 12 cases of congenital hepatic hemangioma and literature review
- PMID: 40356783
- PMCID: PMC12066750
- DOI: 10.3389/fped.2025.1453019
A report of 12 cases of congenital hepatic hemangioma and literature review
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum: A report of 12 cases of congenital hepatic hemangioma and literature review.Front Pediatr. 2025 Jun 9;13:1629270. doi: 10.3389/fped.2025.1629270. eCollection 2025. Front Pediatr. 2025. PMID: 40551783 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Objective: To investigate the clinical features, complications, diagnosis and management of congenital hepatic hemangiomas(CHHs).
Methods: 12 neonates of CHH admitted to our hospital in the past 10 years were retrospectively analyzed, and the clinical manifestations, auxiliary examination results, diagnosis and treatment methods, clinical efficacy andprognosis were reviewed.
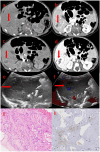
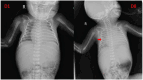
Results: In this study, 12 neonates with CHHs were reported. Among them, 8 cases underwent surgical treatment and recovered well postoperatively. 3 cases received routine pharmacological treatment, were gradually recovering. Only one case, presenting with giant CHH and congestive heart failure (CHF) at birth, failed initial pharmacological treatment and underwent percutaneous hepatic hemangioma embolization but died postoperatively.
Conclusion: Large CHHs tend to be complicated with refractory congestive heart failure, likely due to tumor size and intra-tumor arteriovenous shunt. Propranolol is effective for CHHs with stable hemodynamics but has a slow onset of action, making it less suitable for cases complicated with CHF. Surgical resection is effective and recommended for large CHHs with stable hemodynamics, while percutaneous hepatic hemangioma embolization is advised for unstable cases.
Keywords: congenital hepatic hemangioma; congestive heart failure; percutaneous hepatic hemangioma embolization; propranolol; surgical resection.
© 2025 Wei, Rong, Gao and Chen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Yan W, Li Z, Yang F, Huang X. Analysis on epidemiological and clinical features of 2761 cases of infantile hemangioma. J Pract Dermatol. (2018) 11(02):71–3. 10.11786/sypfbxzz.1674-1293.20180203 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

