Current status of next-generation vaccines against mpox virus: a scoping review
- PMID: 40356988
- PMCID: PMC12066571
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1533533
Current status of next-generation vaccines against mpox virus: a scoping review
Abstract
Introduction: The mpox disease, caused by the mpox virus (MPXV), has become a rising public health issue due to its potential to cause outbreaks. Consistently, this investigation aims to evaluate the current advances in the development of novel immunotherapeutic approaches against MPXV, which are crucial for preventing and controlling mpox spread.
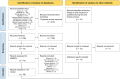
Methods: This scoping review was performed by analyzing the content of English-language articles published between 2018 and 2024, which reported the development of next-generation vaccines against MPXV and their assessment in animal models. Patents within the scope of this research were also included. Contrarywise, studies based solely on immunoinformatic methods, reviews, book chapters, news, and others were excluded. The literature search was executed in 11 databases, such as Scopus, MEDLINE, and PubMed.
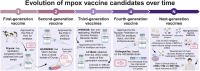
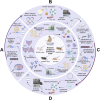
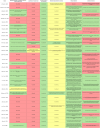
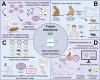
Results: A total of 36 records (32 studies and 4 patents) were included in this review. All 32 articles contain preclinical studies with varied group sizes (4-16) in which the main animal models were BALB/c mice. Less commonly used models included CAST/Ei mice and cynomolgus macaques. Moreover, most vaccines targeted one or more MPXV antigens, such as A29L, A35R, B6R, and M1R, through active immunization (via mRNAs or recombinant antigens) or passive immunization (antibody delivery).
Conclusion: Overall, new generation vaccines might represent prospective candidates to combat the mpox health concern. Nonetheless, several of the analyzed studies possess drawbacks, including animal models with limited similarity to humans, small group sizes, and brief follow-up durations. Consequently, additional research is required to ascertain the long-term protection, efficacy, and safety of these immunotherapeutic approaches.
Keywords: antibody; immunotherapy; mRNA therapeutics; mpox virus; recombinant antigen; vaccine.
Copyright © 2025 Bravo-Vázquez, Bernal-Vázquez, Duttaroy and Paul.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Long-Lasting Protection and Dose Optimization of MPXV Polyvalent Mpox mRNA Vaccines Against Lethal Vaccinia Virus Challenge in Mice.J Med Virol. 2025 Jan;97(1):e70143. doi: 10.1002/jmv.70143. J Med Virol. 2025. PMID: 39726255
-
Single-chain A35R-M1R-B6R trivalent mRNA vaccines protect mice against both mpox virus and vaccinia virus.EBioMedicine. 2024 Nov;109:105392. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2024.105392. Epub 2024 Oct 18. EBioMedicine. 2024. PMID: 39423738 Free PMC article.
-
Polyvalent mpox mRNA vaccines elicit robust immune responses and confer potent protection against vaccinia virus.Cell Rep. 2024 Jun 25;43(6):114269. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2024.114269. Epub 2024 May 23. Cell Rep. 2024. PMID: 38787725
-
Immunogenic proteins and potential delivery platforms for mpox virus vaccine development: A rapid review.Int J Biol Macromol. 2023 Aug 1;245:125515. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.125515. Epub 2023 Jun 21. Int J Biol Macromol. 2023. PMID: 37353117 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mpox global health emergency: Insights into the virus, immune responses, and advancements in vaccines PART II: Insights into the advancements in vaccines.Asian Pac J Allergy Immunol. 2024 Sep;42(3):191-206. doi: 10.12932/AP-111024-1946. Asian Pac J Allergy Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39417768 Review.
Cited by
-
Efficacy of modified-vaccinia Ankara vaccine as pre- and post-exposure prophylaxis against monkeypox sexual transmission in non-human primate model.Nat Commun. 2025 Aug 7;16(1):7306. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-62681-2. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 40775237 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

