Prediction of pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic properties of aldosterone synthase inhibitors at drug discovery stage using an artificial intelligence-physiologically based pharmacokinetic model
- PMID: 40356995
- PMCID: PMC12066422
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1578117
Prediction of pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic properties of aldosterone synthase inhibitors at drug discovery stage using an artificial intelligence-physiologically based pharmacokinetic model
Abstract
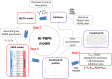
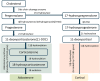
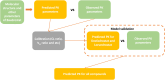
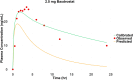
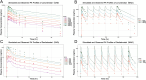
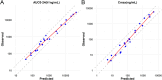
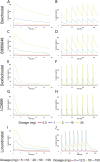
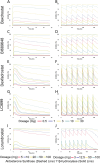
The objective of this study is to develop an artificial intelligence-physiologically based pharmacokinetic (AI-PBPK) model to predict the pharmacokinetic (PK) and pharmacodynamic (PD) properties of aldosterone synthase inhibitors (ASIs), enabling selection of the right candidate with high potency and good selectivity at the drug discovery stage. On a web-based platform, an AI-PBPK model, integrating machine learning and a classical PBPK model for the PK simulation of ASIs, was developed. Baxdrostat, with the most clinical data available, was selected as the model compound. Following calibration and validation using published data, the model was applied to estimate the PK parameters of Baxdrostat, Dexfadrostat, Lorundrostat, BI689648, and the 11β-hydroxylase inhibitor LCI699. The PD of all five compounds was predicted based on plasma free drug concentrations. The results demonstrated that the PK/PD properties of an ASI could be inferred from its structural formula within a certain error range, providing a reference for early ASI lead compounds screening and optimization. Further validation and refinement of this model will enhance its predictive accuracy and expand its application in drug discovery.
Keywords: AI-PBPK; CYP11B2; PK/PD simulation; aldosterone synthase inhibitors; machine learning.
Copyright © 2025 Zhang, Wu, Long, Jin and Liu.
Conflict of interest statement
Author KW was employed by Yinghan Pharmaceutical Technology (Shanghai) Co., Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Andersen K., Hartman D., Peppard T., Hermann D., Van Ess P., Lefkowitz M., et al. (2012). The effects of aldosterone synthase inhibition on aldosterone and cortisol in patients with hypertension: a phase II, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter study. J. Clin. Hypertens. (Greenwich) 14 (9), 580–587. 10.1111/j.1751-7176.2012.00667.x - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Arafat M., Sarfraz M., AbuRuz S. J. P. (2021). Development and in vitro evaluation of controlled release Viagra® containing Poloxamer-188 using Gastroplus™ PBPK modeling software for in vivo predictions and pharmacokinetic assessments. Pharm. Basel, Switz. 14 (5), 479. 10.3390/ph14050479 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Azzam K. A. (2023). SwissADME and pkCSM webservers predictors: an integrated online platform for accurate and comprehensive predictions for in silico ADME/T properties of artemisinin and its derivatives. Kompleksnoe Ispolzovanie Mineralnogo Syra= Complex use mineral Resour. 325 (2), 14–21. 10.31643/2023/6445.13 - DOI
-
- Balhara A., Kale S., Singh S. (2022). “Physiologically based parmacokinetic (PBPK) modelling,” in Computer aided pharmaceutics and drug delivery: an application guide for students and researchers of pharmaceutical sciences. Editor Saharan V. (Singapore: Springer Nature Singapore; ), 255–284.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

