The two cut-offs approach for plasma p-tau217 in detecting Alzheimer's disease in subjective cognitive decline and mild cognitive impairment
- PMID: 40357140
- PMCID: PMC12066393
- DOI: 10.1002/dad2.70116
The two cut-offs approach for plasma p-tau217 in detecting Alzheimer's disease in subjective cognitive decline and mild cognitive impairment
Abstract
Background: The study aimed to explore the applicability of plasma phosphorylated tau (p-tau)217 in identifying patients with subjective cognitive decline (SCD) and mild cognitive impairment (MCI) carrying Alzheimer's disease (AD) pathology in real-world settings.
Methods: Fifty SCD, 87 MCI, and 50 AD-demented patients underwent blood collection to dose plasma p-tau217 with a fully automated Lumipulse G600II assay. Patients were classified according to the Revised Criteria of the Alzheimer's Association Workgroup as Core1+ or Core1- (based on amyloid positron emission tomography, cerebrospinal fluid [CSF] amyloid beta [Aβ]42/Aβ40, CSF p-tau181/Aβ42).
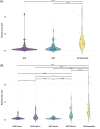
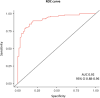
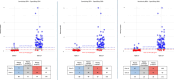
Results: Plasma p-tau217 was accurate for discriminating between Core1+ and Core1- patients (area under the curve = 0.92) with an optimal cut-off value of 0.274 pg/mL, revealing good accuracy (86.29%), positive predictive value (PPV; 88.18%), and negative predictive value (NPV; 83.09%). The two cut-offs approach (0.229-0.516 pg/mL) showed higher accuracy (91.11%), a PPV of 96.25% and a NPV of 83.63%.
Conclusion: The two cut-offs approach provides for stronger accuracy, PPV, and NPV than a single cut-off, making reliable the clinical application of plasma p-tau217 for early detection of AD in real-world settings.
Highlights: Plasma phosphorylated tau (p-tau)217 was highly accurate in detecting Alzheimer's disease (AD) pathology.The two cut-offs approach increased plasma p-tau217 accuracy for AD diagnosis.Even when measured with immunoassay, p-tau217 is a good biomarker for AD diagnosis.Transition of p-tau217 from research setting to clinical practice seems feasible.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease; mild cognitive impairment; plasma biomarkers; plasma phosphorylated tau 217; subjective cognitive decline.
© 2025 The Author(s). Alzheimer's & Dementia: Diagnosis, Assessment & Disease Monitoring published by Wiley Periodicals, LLC on behalf of Alzheimer's Association.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests. Author disclosures are available in the supporting information.
Figures


References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
