Prehabilitation is effective in relieving pain after knee arthroplasty, but has little effect on length of stay and knee function: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
- PMID: 40357305
- PMCID: PMC12066442
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1457407
Prehabilitation is effective in relieving pain after knee arthroplasty, but has little effect on length of stay and knee function: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Abstract
Purpose: The efficacy of preoperative rehabilitation (prehabilitation) for patients undergoing knee arthroplasty remains controversial. Prehabilitation is defined as the implementation of functional exercises, health education, and preemptive medication before surgery to improve postoperative outcomes, typically compared to conventional care protocols. Existing studies have reported inconsistent results regarding its benefits. This meta-analysis aims to evaluate the impact of prehabilitation on hospital length of stay, postoperative pain, and knee function in patients undergoing knee arthroplasty.
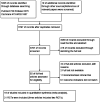
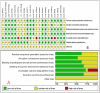
Methods: PubMed, Cochrane, Embase, and Web of Science were searched from their establishment to 16 January 2024. An additional 19 articles were obtained by reading the relevant literature or by a reference search. All clinical randomized controlled trials (RCTs) related to the prehabilitation of total knee arthroplasty were included. All trials were analyzed by two independent reviewers, and the resulting data were analyzed using a random effects model and processed using Review Manager5.4 statistical software. The main outcome measures are as follows: visual analog scale(VAS), knee flexion and extension, and length of stay (LOS).
Results: A total of 18 articles, encompassing 21 RCTs with 2,150 participants (1,167 in the prehabilitation group and 983 in the control group), were included. The analysis revealed that prehabilitation significantly reduced postoperative pain at 1, 3, and 6 months, as evidenced by lower VAS scores. Improvements in knee function were noted in terms of knee extension at 1 month and knee flexion at 3 months postoperatively. However, no significant difference was observed in the length of hospital stay.
Conclusion: Prehabilitation before knee arthroplasty effectively alleviates postoperative pain and partially enhances knee function in the early postoperative period but does not significantly affect the length of hospital stay.
Keywords: VAS score; knee arthroplasty; knee flexion and extension; length of stay; prehabilitation.
Copyright © 2025 Zhang, Lu, Yang, Zhu and Hu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


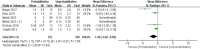
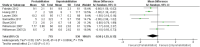

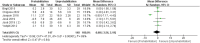


Similar articles
-
The Value of Preoperative Exercise and Education for Patients Undergoing Total Hip and Knee Arthroplasty: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.JBJS Rev. 2017 Dec;5(12):e2. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.RVW.17.00015. JBJS Rev. 2017. PMID: 29232265
-
Is it necessary to perform prehabilitation exercise for patients undergoing total knee arthroplasty: meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Phys Sportsmed. 2018 Feb;46(1):36-43. doi: 10.1080/00913847.2018.1403274. Epub 2017 Nov 15. Phys Sportsmed. 2018. PMID: 29125384
-
Prehabilitation for Patients Undergoing Orthopedic Surgery: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.JAMA Netw Open. 2023 Apr 3;6(4):e238050. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.8050. JAMA Netw Open. 2023. PMID: 37052919 Free PMC article.
-
The Effects of Structured Prehabilitation on Postoperative Outcomes Following Total Hip and Total Knee Arthroplasty: An Overview of Systematic Reviews and Meta-analyses of Randomized Controlled Trials.J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 2025 May;55(5):344-365. doi: 10.2519/jospt.2025.13075. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 2025. PMID: 40298246
-
Physiotherapy rehabilitation after total knee or hip replacement: an evidence-based analysis.Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2005;5(8):1-91. Epub 2005 Jun 1. Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2005. PMID: 23074477 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aytekin E, Sukur E, Oz N, Telatar A, Eroglu Demir S, Sayiner Caglar N, et al. . The effect of a 12 week prehabilitation program on pain and function for patients undergoing total knee arthroplasty: a prospective controlled study. J Clin Orthop Trauma. (2019) 10:345–9. doi: 10.1016/j.jcot.2018.04.006, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zheng Y, Huang Z, Liqun Dai Y, Liu YC, Zhang W, Lin AR. The effect of preoperative rehabilitation training on the early recovery of joint function after artificial Total knee arthroplasty and its effect evaluation. J Healthc Eng. (2022) 2022:1–6. doi: 10.1155/2022/3860991, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- The BMJ . PREHABILITATION, rehabilitation, and revocation in the army. Br Med J. (1946) 1:192–7. PMID: - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

