Structural and functional analysis of a homotrimeric collagen peptide
- PMID: 40357327
- PMCID: PMC12066645
- DOI: 10.3389/fbioe.2025.1575341
Structural and functional analysis of a homotrimeric collagen peptide
Abstract
Objective: This study aimed to chemically synthesize a homotrimeric collagen peptide, evaluate its safety, and assess its effectiveness in promoting collagen synthesis.
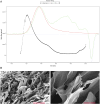
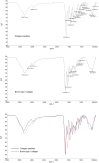
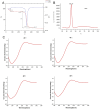
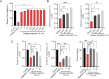
Methods: A homotrimeric collagen peptide was synthesized and structurally characterized using circular dichroism and infrared spectroscopy. Thermal stability was analyzed by TG-DSC, and molecular weight and amino acid composition were determined. In vitro cytotoxicity testing assessed safety, while UV-induced photoaging experiments evaluated its effects on collagen and elastin synthesis. In vivo studies in BALB/c mice examined its impact on collagen content, skin structure, and angiogenesis.
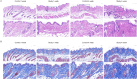
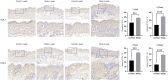
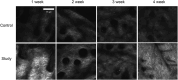
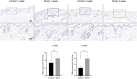
Results: The synthesized collagen peptide exhibited high purity (99.1%) and an amino acid composition of glycine, proline, and hydroxyproline in a balanced ratio (15:17:13). Structural analysis confirmed a stable triple-helical conformation similar to type I collagen with excellent thermal stability (Tm = 326.15°C). Cytotoxicity testing showed no adverse effects on cell viability. In vitro, the peptide significantly enhanced collagen and elastin synthesis in fibroblasts. In vivo, intradermal and subcutaneous injection increased collagen content, improved skin structure, and enhanced microvessel density.
Conclusion: This study presents a chemically synthesized homotrimeric collagen peptide with superior purity, structural stability, and biological efficacy in promoting collagen synthesis. Compared to previous studies, this biomimetic material exhibits exceptional thermal stability (Tm = 326.15°C) and a well-balanced amino acid composition, enabling applications in cosmetics and medical devices requiring heat sterilization (e.g., autoclaving), as validated by our patented method (China Patent No. ZL202410309842.9).
Keywords: collagen peptides; heat stability; homotrimer; safety; synthesis.
Copyright © 2025 Zhang, Li, Lu, Takebayashi, Zhou, Xie, Li, Long, Qin, Zhao and Dong.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors KL, TT, BZ, YL, and XQ were employed by LivingPhoenix Regenerative Technologies Development (Chengdu) Co., Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Bhatwa A., Wang W., Hassan Y. I., Abraham N., Li X.-Z., Zhou T. (2021). Challenges associated with the formation of recombinant protein inclusion bodies in Escherichia coli and strategies to address them for industrial applications. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 9, 630551. 10.3389/fbioe.2021.630551 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

