Exploring the Mechanism of Action of Xuebijing Injection in Treating Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome Based on Network Pharmacology and Animal Experiments
- PMID: 40357382
- PMCID: PMC12067646
- DOI: 10.2147/JIR.S507468
Exploring the Mechanism of Action of Xuebijing Injection in Treating Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome Based on Network Pharmacology and Animal Experiments
Abstract
Objective: To explore the mechanism of Xuebijing injection (XBJ) in treating acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) using network pharmacology and animal experiments.
Methods: Active ingredients of XBJ were analyzed via TCMSP, and ARDS-related targets were identified through DisGENET and Genecard. Intersection targets were obtained using PubChem and Venn diagrams. Protein interaction networks, GO, and KEGG enrichment analyses were conducted. An ARDS rat model was established using lipopolysaccharide (LPS), and rats were divided into control, LPS, and XBJ-treated groups (low, medium, high doses, n=10). Lung wet/dry (W/D) ratio, inflammatory cytokines (IL-17, IL-6, IL-1β, TNF-α), MPO levels, lung pathology, and protein expression of ICAM-1 and HIF-1α were assessed via ELISA, HE staining, immunohistochemistry, and Western blot.
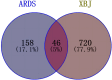
Results: A total of 204 ARDS targets were identified, with 46 intersection targets, mainly TNF-α, MPO, HIF-1α, and ICAM-1. XBJ affected ARDS through IL-17, HIF-1, and TNF signaling pathways. In vivo, LPS-induced lung injury showed alveolar destruction, edema, and inflammation, with increased W/D ratio, cytokines, MPO, and protein expression of HIF-1α and ICAM-1 (P<0.05). XBJ treatment alleviated lung damage, reduced inflammation, and improved pathology in a dose-dependent manner (P<0.05).
Conclusion: XBJ alleviates ARDS by regulating immune function, oxidative stress, and inflammation through IL-17, HIF-1, and TNF pathways.
Keywords: Xuebijing injection; acute respiratory distress syndrome; lipopolysaccharide; network pharmacology.
© 2025 Li et al.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures





Similar articles
-
[Mechanism of Xuebijing Injection in treatment of sepsis-associated ARDS based on network pharmacology and in vitro experiment].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2023 Jun;48(12):3345-3359. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20230202.703. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2023. PMID: 37382018 Chinese.
-
[To explore the preventive and therapeutic effects of Xuebijing injection on acute lung injury induced by cardiopulmonary bypass in rats by regulating the expression of microRNA-17-5p and its mechanism].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2019 Jul;31(7):867-872. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.2095-4352.2019.07.014. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2019. PMID: 31441412 Chinese.
-
Exploring the Molecular Mechanism by which Kaempferol Attenuates Sepsis-related Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome Based on Network Pharmacology and Experimental Verification.Curr Comput Aided Drug Des. 2025;21(2):166-178. doi: 10.2174/0115734099295805240126043059. Curr Comput Aided Drug Des. 2025. PMID: 38321908
-
Analysis of the Efficacy and Mechanism of Action of Xuebijing Injection on ARDS Using Meta-Analysis and Network Pharmacology.Biomed Res Int. 2021 May 22;2021:8824059. doi: 10.1155/2021/8824059. eCollection 2021. Biomed Res Int. 2021. PMID: 34124260 Free PMC article.
-
Xuebijing and somatostatin against acute pancreatitis: A systematic review and network pharmacology.Medicine (Baltimore). 2024 Dec 13;103(50):e40964. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000040964. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024. PMID: 39686429 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

