BeStSel: analysis site for protein CD spectra-2025 update
- PMID: 40357643
- PMCID: PMC12230724
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkaf378
BeStSel: analysis site for protein CD spectra-2025 update
Abstract
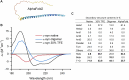
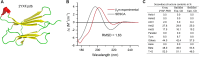
Circular dichroism (CD) spectroscopy is a widely used technique to characterize the secondary structure composition of proteins. We have developed the Beta Structure Selection (BeStSel) method (PNAS, 112, E3095), which solves the main problem of protein CD spectroscopy-namely, the spectral variability of β-structures. The BeStSel web server utilizes this method to provide tools to the community for CD spectrum analysis. BeStSel uniquely provides information on eight secondary structure components, including parallel β-structure and antiparallel β-sheets with three different twist groups. It outperforms all available methods in accuracy and information content, and is also able to predict protein folds down to the topology/homology level of the CATH classification. The algorithm has been further developed, and the accuracy of the estimation of the secondary structure elements is improved by 0.7% as an average on the reference dataset. A new module of the web server calculates protein stability from the thermal denaturation profile followed by CD. Secondary structure calculations of uploaded PDB and mmcif files support the experimental verification of MD simulations and AlphaFold models by CD spectroscopy. Well-proven modules for disorder-order classification and extinction coefficient calculation continue to work. The BeStSel server is freely accessible at https://bestsel.elte.hu.
© The Author(s) 2025. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

