Recent advances in nanocrystals for arthritis drug delivery
- PMID: 40357685
- PMCID: PMC12312752
- DOI: 10.1080/17425247.2025.2505758
Recent advances in nanocrystals for arthritis drug delivery
Abstract
Introduction: More than 500 million people worldwide suffer from arthritis, experiencing daily pain and inflammation. Current treatments for osteoarthritis (OA) and rheumatoid arthritis (RA) are palliative, offering only symptom relief. No disease-modifying OA drugs (DMOADs) capable of restoring joint functionality and regenerating the cartilage matrix have yet been approved by the FDA or EMA.
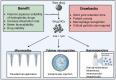
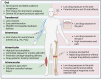
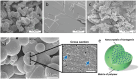
Areas covered: This review highlights recent advances in nanocrystals (NCs) for arthritis drug delivery, including conventional nanosuspensions and novel transdermal microneedles. Special attention is given to intra-articular DMOADs formulated as NC-in-microparticles, designed to extend drug release over months. Papers and reviews with the mentioned contents and published over the last 5 years were included in the review process.
Expert opinion: New DMOADs and disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) are often poorly water-soluble, limiting their clinical progress. The versatility of NCs and nanosuspensions offers a potential advantage over other types of nanoparticles, as they can be adapted to various delivery systems, administration routes, and types of arthritis. Due to the avascular nature of cartilage, exploring the intra-articular route for OA management is essential. Implementing cartilage-targeted strategies or using stimuli-responsive hydrogels can further enhance their therapeutic potential.
Keywords: Nanocrystals; drug delivery; intraarticular; microneedles; microparticles; nanosuspensions; osteoarthritis; rheumatoid arthritis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no relevant affiliations or financial involvement with any organization or entity with a financial interest in or financial conflict with the subject matter or materials discussed in the manuscript. This includes employment, consultancies, honoraria, stock ownership or options, expert testimony, grants or patents received or pending, or royalties.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
