Impact of flushing procedures on drinking water biostability and invasion susceptibility in distribution systems
- PMID: 40358239
- PMCID: PMC12175504
- DOI: 10.1128/aem.00686-25
Impact of flushing procedures on drinking water biostability and invasion susceptibility in distribution systems
Abstract
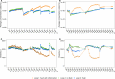
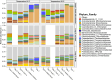
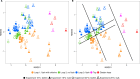
Ensuring high-quality drinking water remains challenging, as complaints about odors, discoloration, or contamination persist. In Belgium and beyond, traditional flushing is a common curative strategy that involves discharging large water volumes through hydrants while the network remains in use. In some cases, free chlorine (0.5 mg/L) is added, and consumers are advised not to drink the water. However, flushing can alter water biostability, potentially increasing susceptibility to microbial invasion. This study used a pilot-scale drinking water distribution system with three identical 100 m polyvinyl chloride(PVC) loops (DN 80 mm) to assess the impact of flushing with and without chlorination as practiced in chlorinated networks. Loop 1 was flushed with tap water and sodium hypochlorite (NaOCl), followed by two non-chlorinated flushes, loop 2 was unflushed, and loop 3 underwent three flushes. Biostability was assessed using online flow cytometry, and susceptibility to bacterial invasion (Aeromonas media, Pseudomonas putida, and Serratia fonticola) was evaluated in the days following flushing. The water had a 7-day residence time. Results showed that chlorinated flushing promoted microbial regrowth (3.8 × 105 vs 2.0 × 105 and 1.6 × 105 cells/mL for loops 1, 2, and 3, respectively), primarily of resident Sphingopyxis spp. Biofilm cell densities (~4 × 106 cells/cm2) remained stable across conditions. Bacterial indicators declined over time, with P. pudita and S. fonticola surviving longer (>100 hours) than A. media (13 hours). Decay rates were highest in chlorinated loops, likely due to increased microbial competition. For example, the decay constant of S. fonticola at 20°C was -0.082 h-1, -0.042 h-1, and -0.027 h-1 for loops 1, 2, and 3, respectively.
Importance: Traditional flushing is used as a curative strategy to solve unwanted quality issues during distribution, yet its impact on microbial biostability remains poorly understood. This study provides critical insights into how traditional flushing, both with and without chlorination, influences microbial regrowth and susceptibility to invasion. Findings reveal that chlorinated flushing promotes the regrowth of resident drinking water bacteria while accelerating the decay of introduced unwanted bacterial indicators, emphasizing the complex trade-off between microbial control and system stability. Understanding these dynamics is essential for optimizing flushing procedures, minimizing unintended consequences, and improving distribution system resilience.
Keywords: biofilm; biostability; drinking water microbiology; flushing; invasion.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Favere J, Barbosa RG, Sleutels T, Verstraete W, De Gusseme B, Boon N. 2021. Safeguarding the microbial water quality from source to tap. npj Clean Water 4:1–6. doi: 10.1038/s41545-021-00118-1 - DOI
-
- Chatzigiannidou I, Props R, Boon N. 2018. Drinking water bacterial communities exhibit specific and selective necrotrophic growth. npj Clean Water 1:1–4. doi: 10.1038/s41545-018-0023-9 - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

