A Systematic Review of Aflatoxin B1 Contamination in Livestock Feed and Detection Methods in Ethiopia
- PMID: 40359229
- PMCID: PMC12073923
- DOI: 10.1002/vms3.70405
A Systematic Review of Aflatoxin B1 Contamination in Livestock Feed and Detection Methods in Ethiopia
Abstract
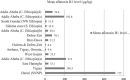
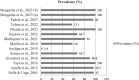
Aflatoxin B1 (AFB1) contamination in Ethiopian livestock feed poses significant risks to both animal and human health due to poor hygiene and inadequate storage practices. This study focuses on specific cereal grains, such as maize and groundnuts, which are commonly used in livestock feed but have been underexplored in terms of their role in AFB1 contamination, especially under local farming and storage conditions. A literature search was conducted from June 2024 to November 2024, utilizing databases like Google Scholar and African Journals Online. Articles were screened on the basis of titles and abstracts, with duplicates removed using EndNote. Only English-language publications from 2000 onwards were included. Quality assessment adhered to Centre for Reviews and Dissemination (CRD) and Cochrane guidelines, and statistical analysis was performed using Statistical Package for the Social Sciences (SPSS). Non-English studies were excluded to focus on accessible research for Ethiopian stakeholders, ensuring the relevance of findings. Out of 96 retrieved works, 79 remained after eliminating duplicates and pre-2000 studies. After screening, 30 full-text articles were assessed, resulting in 16 exclusions. Ultimately, 14 studies, primarily cross-sectional, qualified for review. AFB1 contamination levels varied widely, from 2.4% to 100%, across different regions in Ethiopia. This study underscores the urgent need for robust monitoring and interventions to combat AFB1 contamination in Ethiopian livestock feed. Analysis of covariance (ANCOVA) analysis revealed significant differences in contamination levels based on detection methods, highlighting the need for standardized approaches to ensure consistency in reported findings. This study underscores the urgent need for robust monitoring and interventions to combat AFB1 contamination in Ethiopian livestock feed. Standardized detection methods and aligning Ethiopia's regulations with international standards like Codex Alimentarius are essential for safeguarding public and animal health.
Keywords: Ethiopia; aflatoxin B1; contamination; detection methods; livestock feed; systematic review.
© 2025 The Author(s). Veterinary Medicine and Science published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Al‐Jaal, B. A. , Jaganjac M., Barcaru A., Horvatovich P., and Latiff A. 2019. “Aflatoxin, Fumonisin, Ochratoxin, Zearalenone and Deoxynivalenol Biomarkers in Human Biological Fluids: A Systematic Literature Review, 2001–2018.” Food and Chemical Toxicology 129: 211–228. - PubMed
-
- Assaye, M. , Gemeda N., and Weledesemayat G. 2016. “Aspergillus Species and Aflatoxin Contamination of Pre and Post‐Harvest Maize Grain in West Gojam, Ethiopia.” Journal of Food Science and Nutrtion 2, no. 2: 1–7.
-
- Assefa, D. , Teare M., and Skinnes H. 2012. “Natural Occurrence of Toxigenic Fungi Species and Aflatoxin in Freshly Harvested Groundnut Kernels in Tigray, Northern Ethiopia.” Journal of the Drylands 5, no. 1: 377–384.
-
- Ayelign, A. , Woldegiorgis A. Z., Adish A., and De Saeger S. 2018. “Total Aflatoxins in Complementary Foods Produced at Community Levels Using Locally Available Ingredients in Ethiopia.” Food Additives & Contaminants: Part B 11, no. 2: 111–118. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

