Obesity and heart failure with preserved ejection fraction: focus on new drugs and future direction in medical treatment
- PMID: 40360219
- PMCID: PMC12081111
- DOI: 10.3904/kjim.2024.387
Obesity and heart failure with preserved ejection fraction: focus on new drugs and future direction in medical treatment
Abstract
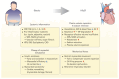
Obesity is a major risk factor for heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) and contributes through multiple pathophysiological pathways, including systemic inflammation, neurohormonal activation, and mechanical inhibition. The treatment of obesity has shown significant potential for improving HFpEF outcomes. Sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors have emerged as effective treatments for improving symptoms and quality of life in patients with HFpEF while aiding in weight control. Furthermore, a recent demonstration of the clinical benefits of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RAs) in HFpEF showed promising results in reducing weight loss, and improving symptoms and clinical outcomes. In this review article, we discuss the association between HFpEF and obesity, the emerging role of GLP-1 RAs, and future directions for medical therapies targeting obesity-associated HFpEF.
Keywords: Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists; Heart failure; Obesity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors disclose no conflicts.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Beyond weight loss: the potential of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists for treating heart failure with preserved ejection fraction.Heart Fail Rev. 2025 Jan;30(1):17-38. doi: 10.1007/s10741-024-10438-2. Epub 2024 Sep 13. Heart Fail Rev. 2025. PMID: 39269643 Review.
-
The role of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor (GLP-1R) agonists in enhancing endothelial function: a potential avenue for improving heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF).Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2025 Feb 7;24(1):70. doi: 10.1186/s12933-025-02607-w. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2025. PMID: 39920668 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparative effects of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists and sodium-glucose co-transporter-2 inhibitors on heart failure with preserved ejection fraction in diabetic patients: a meta-analysis.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2024 Aug 31;23(1):324. doi: 10.1186/s12933-024-02415-8. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2024. PMID: 39217337 Free PMC article.
-
The landscape of novel antidiabetic drugs in diabetic HFpEF: relevant mechanisms and clinical implications.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2025 Apr 28;24(1):186. doi: 10.1186/s12933-025-02750-4. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2025. PMID: 40295996 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Refining the link between obesity and heart failure: insights from GLP-1 receptor agonist trials and studies adopting direct adiposity measures.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2025 May 22;24(1):224. doi: 10.1186/s12933-025-02778-6. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2025. PMID: 40405237 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Seferović PM, Vardas P, Jankowska EA, et al. National Heart Failure Societies of the ESC member countries (see Appendix The Heart Failure Association Atlas: heart failure epidemiology and management statistics 2019. Eur J Heart Fail. 2021;23:906–914. - PubMed
-
- Dunlay SM, Roger VL, Redfield MM. Epidemiology of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2017;14:591–602. - PubMed
-
- Redfield MM. Heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. N Engl J Med. 2017;376:897. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
