Tocilizumab, sarilumab and anakinra in critically ill patients with COVID-19: a randomised, controlled, open-label, adaptive platform trial
- PMID: 40360262
- PMCID: PMC12322455
- DOI: 10.1136/thorax-2024-222488
Tocilizumab, sarilumab and anakinra in critically ill patients with COVID-19: a randomised, controlled, open-label, adaptive platform trial
Abstract
Introduction: Tocilizumab improves outcomes in critically ill patients with COVID-19. Whether other immune-modulator strategies are equally effective or better is unknown.
Methods: We investigated treatment with tocilizumab, sarilumab, anakinra and no immune modulator in these patients. In this ongoing, adaptive platform trial in 133 sites in 9 countries, we randomly assigned patients with allocation ratios dependent on the number of interventions available at each site. The primary outcome was an ordinal scale combining in-hospital mortality (assigned -1) and days free of organ support to day 21 in survivors. The trial used a Bayesian statistical model with predefined triggers for superiority, inferiority, efficacy, equivalence or futility.
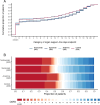
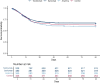
Results: Of 2274 critically ill participants enrolled between 25 March 2020 and 10 April 2021, 972 were assigned to tocilizumab, 485 to sarilumab, 378 to anakinra and 418 to control. Median organ support-free days were 7 (IQR -1, 16), 9 (IQR -1, 17), 0 (IQR -1, 15) and 0 (IQR -1, 15) for tocilizumab, sarilumab, anakinra and control, respectively. Median adjusted ORs were 1.46 (95% credible intervals (CrI) 1.13, 1.87), 1.50 (95% CrI 1.13, 2.00) and 0.99 (95% CrI 0.74, 1.35) for tocilizumab, sarilumab and anakinra relative to control, yielding 99.8%, 99.8% and 46.6% posterior probabilities of superiority, respectively, compared with control. All treatments appeared safe.
Conclusions: In critically ill patients with COVID-19, tocilizumab and sarilumab have equivalent effectiveness at reducing duration of organ support and death. Anakinra is not effective in this population.
Trial registration number: NCT02735707.
Keywords: COVID-19; Critical Care; Pneumonia.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2025. Re-use permitted under CC BY. Published by BMJ Group.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: ACG is funded by an NIHR Research Professorship (RP-2015-06-18) and MS-H by an NIHR Clinician Scientist Fellowship (CS-2016-16-011). SYCT is supported by an Australian National Health and Medical Research Council Career Development Fellowship (#APP1145033). AMT is supported by NUHS research funding and NMRC SHC funding (CSAINV20NOV-0014). ACC is supported by an NHMRC Investigator Grant (APP1194678). Roche Products, Sanofi (Aventis Pharma), Swedish Orphan Biovitrum AB (Sobi), and Faron Pharmaceuticals supported the trial through the provision of drugs in some countries.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
