O-GlcNAcylation of NONO regulates paraspeckle component assembly and contributes to colon cancer cell proliferation
- PMID: 40360465
- PMCID: PMC12075841
- DOI: 10.1038/s41420-025-02405-z
O-GlcNAcylation of NONO regulates paraspeckle component assembly and contributes to colon cancer cell proliferation
Abstract
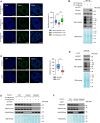
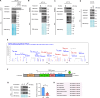
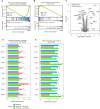
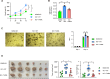
Non-POU domain-containing octamer-binding protein (NONO) is a multifunctional member of the Drosophila behavior/human splicing (DBHS) protein family with DNA- and RNA-binding activity. NONO is highly expressed in various types of cancer, and excessive O-GlcNAcylation has also been implicated in tumorigenesis. Although recent studies revealed that NONO is O-GlcNAcylated and that this modification is involved in DNA damage repair, it remains unknown whether O-GlcNAcylation of NONO regulates cancer cell proliferation. Additionally, little is known about the effect of O-GlcNAcylation on other biological properties of NONO. In this study, we identify Thr440 as the primary NONO O-GlcNAcylation site and demonstrates its crucial role in the assembly of paraspeckles, an important subnuclear compartment that facilitates NONO-dependent transcriptional regulation in mammalian cells. Moreover, we found that O-GlcNAcylation of NONO is required to maintain the expression of genes related to microtubule cytoskeleton organization involved in mitosis and to suppress the expression of genes related to cellular response to type I interferon. Regarding the regulation of these genes, depletion of NONO O-GlcNAcylation at Thr440 significantly inhibited the proliferation of colon cancer cells. Collectively, our findings highlight NONO O-GlcNAcylation as a key regulator modulating paraspeckle formation and as a candidate therapeutic target in colon cancer.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests. Ethics approval: All methods were performed in accordance with the relevant guidelines and regulations. All experimental protocols were approved by the The Institutional Animal Care and Use Committees of the Laboratory Animal Research Center at Yonsei University (Approval Numbers: IACUC-A-202107-1286-02, IACUC-A-202205-1470-01). Our manuscript does not contain any human data.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Paraspeckle subnuclear bodies depend on dynamic heterodimerisation of DBHS RNA-binding proteins via their structured domains.J Biol Chem. 2022 Nov;298(11):102563. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2022.102563. Epub 2022 Oct 7. J Biol Chem. 2022. PMID: 36209820 Free PMC article.
-
Structure of the heterodimer of human NONO and paraspeckle protein component 1 and analysis of its role in subnuclear body formation.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012 Mar 27;109(13):4846-50. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1120792109. Epub 2012 Mar 13. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012. PMID: 22416126 Free PMC article.
-
NONO and tumorigenesis: More than splicing.J Cell Mol Med. 2020 Apr;24(8):4368-4376. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.15141. Epub 2020 Mar 13. J Cell Mol Med. 2020. PMID: 32168434 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Crystallization of a paraspeckle protein PSPC1-NONO heterodimer.Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun. 2011 Oct 1;67(Pt 10):1231-4. doi: 10.1107/S1744309111026212. Epub 2011 Sep 29. Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun. 2011. PMID: 22102035 Free PMC article.
-
Established and Evolving Roles of the Multifunctional Non-POU Domain-Containing Octamer-Binding Protein (NonO) and Splicing Factor Proline- and Glutamine-Rich (SFPQ).J Dev Biol. 2024 Jan 5;12(1):3. doi: 10.3390/jdb12010003. J Dev Biol. 2024. PMID: 38248868 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Fox AH, Lam YW, Leung AKL, Lyon CE, Andersen J, Mann M, et al. Paraspeckles: a novel nuclear domain. Curr Biol. 2002;12:13–25. 10.1016/S0960-9822(01)00632-7. - PubMed
-
- Fox AH, Nakagawa S, Hirose T, Bond CS. Paraspeckles: where long noncoding RNA meets phase separation. Trends Biochemical Sci. 2018;43:124–35. 10.1016/j.tibs.2017.12.001. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

