PEDOT:PSS-based bioelectronics for brain monitoring and modulation
- PMID: 40360495
- PMCID: PMC12075682
- DOI: 10.1038/s41378-025-00948-w
PEDOT:PSS-based bioelectronics for brain monitoring and modulation
Abstract
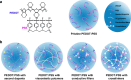
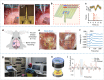
The growing demand for advanced neural interfaces that enable precise brain monitoring and modulation has catalyzed significant research into flexible, biocompatible, and highly conductive materials. PEDOT:PSS-based bioelectronic materials exhibit high conductivity, mechanical flexibility, and biocompatibility, making them particularly suitable for integration into neural devices for brain science research. These materials facilitate high-resolution neural activity monitoring and provide precise electrical stimulation across diverse modalities. This review comprehensively examines recent advances in the development of PEDOT:PSS-based bioelectrodes for brain monitoring and modulation, with a focus on strategies to enhance their conductivity, biocompatibility, and long-term stability. Furthermore, it highlights the integration of multifunctional neural interfaces that enable synchronous stimulation-recording architectures, hybrid electro-optical stimulation modalities, and multimodal brain activity monitoring. These integrations enable fundamentally advancing the precision and clinical translatability of brain-computer interfaces. By addressing critical challenges related to efficacy, integration, safety, and clinical translation, this review identifies key opportunities for advancing next-generation neural devices. The insights presented are vital for guiding future research directions in the field and fostering the development of cutting-edge bioelectronic technologies for neuroscience and clinical applications.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
Publication types
Grants and funding
- 30802-110690303/Guangdong Science and Technology Department (Science and Technology Department, Guangdong Province)
- 2021ZD0204300/National Science Foundation of China | Major Research Plan
- MYRGGRG2023-00038-FHS/Universidade de Macau (University of Macau)
- 28709-312200502501/Beijing Normal University (BNU)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
