The immune NIK1/RPL10/LIMYB signaling module regulates photosynthesis and translation under biotic and abiotic stresses
- PMID: 40360515
- PMCID: PMC12075613
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-59571-y
The immune NIK1/RPL10/LIMYB signaling module regulates photosynthesis and translation under biotic and abiotic stresses
Abstract
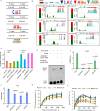
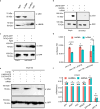
Photosynthesis and translation are targets of metabolic control and development in plants, yet how stress signals coordinately regulate these opposing energy-producing and consuming processes remains enigmatic. Here, we unravel a growth control circuit that ties photosynthesis to translational control in response to biotic and abiotic signals. Our findings reveal that the L10-INTERACTING MYB DOMAIN-CONTAINING PROTEIN (LIMYB), a key player of the NUCLEAR SHUTTLE PROTEIN-INTERACTING KINASE 1 (NIK1)/ RIBOSOMAL PROTEIN L10 (RPL10) antiviral signaling pathway, not only downregulates translation genes, but also represses photosynthesis-related genes and photosynthesis itself. LIMYB repressor activity, regulated by phosphorylation, is crucial for the decline in photosynthesis under stress. NIK1 activation by PAMPs or the phosphomimetic NIK1-T474D represses photosynthesis-related genes and photosynthesis in control but not in limyb lines. Furthermore, heat and osmotic stress also activate the NIK1/RPL10/LIMYB signaling circuit in wild type. These stresses induce NIK1 phosphorylation, but not marker gene repression, in limyb, indicating that LIMYB connects NIK1 activation to stress-mediated downregulation of translation- and photosynthesis-related genes. This coordinated repression via the NIK1/RPL10/LIMYB module may help plants adapt to changing environments.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures






Similar articles
-
NIK1-mediated translation suppression functions as a plant antiviral immunity mechanism.Nature. 2015 Apr 30;520(7549):679-82. doi: 10.1038/nature14171. Epub 2015 Feb 23. Nature. 2015. PMID: 25707794 Free PMC article.
-
NIK1, a host factor specialized in antiviral defense or a novel general regulator of plant immunity?Bioessays. 2015 Nov;37(11):1236-42. doi: 10.1002/bies.201500066. Epub 2015 Sep 3. Bioessays. 2015. PMID: 26335701
-
Regulated nuclear trafficking of rpL10A mediated by NIK1 represents a defense strategy of plant cells against virus.PLoS Pathog. 2008 Dec;4(12):e1000247. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1000247. Epub 2008 Dec 26. PLoS Pathog. 2008. PMID: 19112492 Free PMC article.
-
Multiple Functions of MYB Transcription Factors in Abiotic Stress Responses.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jun 7;22(11):6125. doi: 10.3390/ijms22116125. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34200125 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SERKs and NIKs: Coreceptors or signaling hubs in a complex crosstalk between growth and defense?Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2024 Feb;77:102447. doi: 10.1016/j.pbi.2023.102447. Epub 2023 Sep 8. Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2024. PMID: 37690927 Review.
References
-
- Reinbothe, C., Pollmann, S. & Reinbothe, S. Singlet oxygen signalling links photosynthesis to translation and plant growth. Trends Plant Sci.15, 499–506 (2010). - PubMed
-
- Tcherkez, G. et al. Protein synthesis increases with photosynthesis via the stimulation of translation initiation. Plant Sci.291, 110352 (2020). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

