pS396/pS404 (PHF1) tau vaccine outperforms pS199/pS202 (AT8) in rTg4510 tauopathy model
- PMID: 40360566
- PMCID: PMC12075828
- DOI: 10.1038/s41541-025-01147-4
pS396/pS404 (PHF1) tau vaccine outperforms pS199/pS202 (AT8) in rTg4510 tauopathy model
Abstract
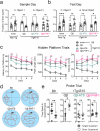
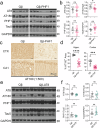
Tauopathies, including Alzheimer's disease (AD) and Frontotemporal Dementia (FTD), are histopathologically defined by the aggregation of hyperphosphorylated pathological tau (pTau) as neurofibrillary tangles in the brain. Site-specific phosphorylation of tau occurs early in the disease process and correlates with progressive cognitive decline, thus serving as targetable pathological epitopes for immunotherapy development. Previously, we developed a vaccine (Qβ-pT181) displaying phosphorylated Thr181 tau peptides on the surface of a Qβ bacteriophage virus-like particle (VLP) that induced robust antibody responses, cleared pathological tau, and rescued memory deficits in a transgenic mouse model of tauopathy. Here we report the characterization and comparison of two additional Qβ VLP-based vaccines targeting the dual phosphorylation sites Ser199/Ser202 (Qβ-AT8) and Ser396/Ser404 (Qβ-PHF1). Both Qβ-AT8 and Qβ-PHF1 vaccines elicited high-titer antibody responses against their pTau epitopes. However, only Qβ-PHF1 rescued cognitive deficits, reduced soluble and insoluble pathological tau, and inflammatory microgliosis in a 4.5-month rTg4510 model of FTD. Both sera from Qβ-AT8 and Qβ-PHF1 vaccinated mice were specifically reactive to tau pathology in human AD post-mortem brain sections. These studies further support the use of VLP-based immunotherapies to target pTau in AD and related tauopathies and provide potential insight into the clinical efficacy of various pTau epitopes in the development of immunotherapies.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Update of
-
Virus-like particle (VLP)-based vaccine targeting tau phosphorylated at Ser396/Ser404 (PHF1) site outperforms phosphorylated S199/S202 (AT8) site in reducing tau pathology and restoring cognitive deficits in the rTg4510 mouse model of tauopathy.Res Sq [Preprint]. 2024 Jun 12:rs.3.rs-4390998. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-4390998/v1. Res Sq. 2024. Update in: NPJ Vaccines. 2025 May 13;10(1):94. doi: 10.1038/s41541-025-01147-4. PMID: 38946961 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Alzheimer, A., Stelzmann, R. A., Schnitzlein, H. N. & Murtagh, F. R. An English translation of Alzheimer’s 1907 paper, ‘Uber eine eigenartige Erkankung der Hirnrinde’. Clin. Anat.8, 429–431 (1995). - PubMed
-
- Pevalova, M., Filipcik, P., Novak, M., Avila, J. & Iqbal, K. Post-translational modifications of tau protein. Bratisl. Lek. Listy107, 346–353 (2006). - PubMed
Grants and funding
- P20GM109089/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of General Medical Sciences (NIGMS)
- P20 GM109089/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01NS083704/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS)
- P30AG086404/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute on Aging (U.S. National Institute on Aging)
- L70AA030440/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism (NIAAA)
- R01 NS083704/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AI007538/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- RF1NS083704/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS)
- K12 GM088021/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- K12GM088021-10/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of General Medical Sciences (NIGMS)
- L70 AA030440/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG086404/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- RF1 NS083704/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

