Early detection of mental health disorders using machine learning models using behavioral and voice data analysis
- PMID: 40360580
- PMCID: PMC12075568
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-00386-8
Early detection of mental health disorders using machine learning models using behavioral and voice data analysis
Abstract
People of all demographics are impacted by mental illness, which has become a widespread and international health problem. Effective treatment and support for mental illnesses depend on early discovery and precise diagnosis. Notably, delayed diagnosis may lead to suicidal thoughts, destructive behaviour, and death. Manual diagnosis is time-consuming and laborious. With the advent of AI, this research aims to develop a novel mental health disorder detection network with the objective of maximum accuracy and early discovery. For this reason, this study presents a novel framework for the early detection of mental illness disorders using a multi-modal approach combining speech and behavioral data. This framework preprocesses and analyzes two distinct datasets to handle missing values, normalize data, and eliminate outliers. The proposed NeuroVibeNet combines Improved Random Forest (IRF) and Light Gradient-Boosting Machine (LightGBM) for behavioral data and Hybrid Support Vector Machine (SVM) and K-Nearest Neighbors (KNN) for voice data. Finally, a weighted voting mechanism is applied to consolidate predictions. The proposed model achieves robust performance and a competitive accuracy of 99.06% in distinguishing normal and pathological conditions. This framework validates the feasibility of multi-modal data integration for reliable and early mental illness detection.
Keywords: Behavioral data; Deep learning; Machine learning; Mental health disorders; Voice data.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
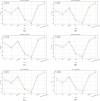
Figures





Similar articles
-
AI-driven early diagnosis of specific mental disorders: a comprehensive study.Cogn Neurodyn. 2025 Dec;19(1):70. doi: 10.1007/s11571-025-10253-x. Epub 2025 May 5. Cogn Neurodyn. 2025. PMID: 40330715 Free PMC article.
-
An integrated approach of feature selection and machine learning for early detection of breast cancer.Sci Rep. 2025 Apr 15;15(1):13015. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-97685-x. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40234520 Free PMC article.
-
Prediction and Diagnosis of Breast Cancer Using Machine and Modern Deep Learning Models.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2024 Mar 1;25(3):1077-1085. doi: 10.31557/APJCP.2024.25.3.1077. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2024. PMID: 38546090 Free PMC article.
-
PROTA: A Robust Tool for Protamine Prediction Using a Hybrid Approach of Machine Learning and Deep Learning.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Sep 24;25(19):10267. doi: 10.3390/ijms251910267. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39408595 Free PMC article.
-
Meta-analysis of voice disorders databases and applied machine learning techniques.Math Biosci Eng. 2020 Nov 11;17(6):7958-7979. doi: 10.3934/mbe.2020404. Math Biosci Eng. 2020. PMID: 33378928
References
-
- Merino, M. et al. Body perceptions and psychological well-being: A review of the impact of social media and physical measurements on self-esteem and mental health with a focus on body image satisfaction and its relationship with cultural and gender factors. Healthcare12(14), 1396 (2024). - PMC - PubMed
-
- Pourkeyvan, A., Safa, R. & Sorourkhah, A. Harnessing the power of hugging face transformers for predicting mental health disorders in social networks. IEEE Access12, 28025–28035 (2024).
-
- Khan, S. & Alqahtani, S. Hybrid machine learning models to detect signs of depression. Multimed. Tools Appl.83(13), 38819–38837 (2024).
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

