Development and internal validation of a prediction model for rheumatoid arthritis: a case-control study
- PMID: 40360585
- PMCID: PMC12075644
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-00816-7
Development and internal validation of a prediction model for rheumatoid arthritis: a case-control study
Abstract
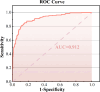
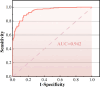
This study measured sociodemographic characteristics, dietary habits, lifestyle habits, genetics, and other factors that may contribute to the development of Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA). Independent risk factors for RA were identified by logistic regression analysis, and a prediction model was constructed. The area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC) was used to evaluate the prediction accuracy of the model, and the calibration of the model was evaluated by the Hosmer-Lemeshow test. A total of 432 participants, comprising 216 healthy individuals and 216 patients diagnosed with RA at two hospitals in Sichuan, China, from March 2022 to January 2023 were included in this study. Logistic regression analysis revealed that occupation type, place of residence, history of mumps, dietary combination, sweet, damp dwelling, fish, vaccine history, and rs805297 were significantly associated with the pathogenesis of RA. The model constructed in this study showed good prediction, with an AUC of 0.912. The Youden index was 0.699, the sensitivity was 0.847 and the specificity was 0.852. The Hosmer-Lemeshow test results (χ2 = 8.441, P = 0.392) indicated that the model had good diagnostic value. The internal validation AUC was 0.942. We propose a new promising model for identifying individuals at risk of developing RA.
Keywords: Case-control study; Rheumatoid arthritis; Risk assessment; Risk factors; Risk prediction model.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests. Ethics approval and consent to participate: This study was approved by the Ethics Review Committee and conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki. After review by the Ethics Committee on Biomedical Research, West China Hospital of Sichuan University, the study officially started with the ethical review number 2021 (175). The data used is considered anonymized. The study confirmed that informed consent was obtained from all subjects or their legal guardians. Consent for publication: N/A (no identifiable information is published).
Figures
References
-
- Smolen, J. S., Aletaha, D. & McInnes, I. B. Rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet388, 2023–2038 (2016). - PubMed
-
- Zeng, X. F., Zhu, S. L., Tan, A. C. & Xie, X. P. A systematic evaluation of rheumatoid arthritis disease burden and quality of life in China. A systematic evaluation of studies on disease burden and quality of survival of rheumatoid arthritis in China. Chinese Journal of Evidence-Based Medicine 13, 300–307 (2013). (2011).
-
- Sokka, T., Abelson, B. & Pincus, T. Mortality in rheumatoid arthritis: 2008 update. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol.26, S35–61 (2008). - PubMed
-
- Hu, K. et al. Prevalence of rheumatoid arthritis among rural residents aged 20–79 years and risk factors in Qiannan, Guizhou. China Public. Health. 35, 813–817 (2019).
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical