Leveraging explainable artificial intelligence with ensemble of deep learning model for dementia prediction to enhance clinical decision support systems
- PMID: 40360623
- PMCID: PMC12075694
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-97102-3
Leveraging explainable artificial intelligence with ensemble of deep learning model for dementia prediction to enhance clinical decision support systems
Abstract
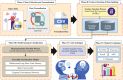
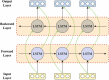
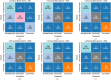
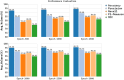
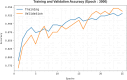
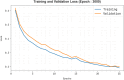
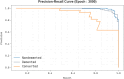
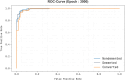
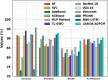
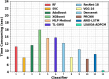
The prevalence of dementia is growing worldwide due to the fast ageing of the population. Dementia is an intricate illness that is frequently produced by a mixture of genetic and environmental risk factors. There is no treatment for dementia yet; therefore, the early detection and identification of persons at greater risk of emerging dementia becomes crucial, as this might deliver an opportunity to adopt lifestyle variations to decrease the risk of dementia. Many dementia risk prediction techniques to recognize individuals at high risk have progressed in the past few years. Accepting a structure uniting explainability in artificial intelligence (XAI) with intricate systems will enable us to classify analysts of dementia incidence and then verify their occurrence in the survey as recognized or suspected risk factors. Deep learning (DL) and machine learning (ML) are current techniques for detecting and classifying dementia and making decisions without human participation. This study introduces a Leveraging Explainability Artificial Intelligence and Optimization Algorithm for Accurate Dementia Prediction and Classification Model (LXAIOA-ADPCM) technique in medical diagnosis. The main intention of the LXAIOA-ADPCM technique is to progress a novel algorithm for dementia prediction using advanced techniques. Initially, data normalization is performed by utilizing min-max normalization to convert input data into a beneficial format. Furthermore, the feature selection process is performed by implementing the naked mole-rat algorithm (NMRA) model. For the classification process, the proposed LXAIOA-ADPCM model implements ensemble classifiers such as the bidirectional long short-term memory (BiLSTM), sparse autoencoder (SAE), and temporal convolutional network (TCN) techniques. Finally, the hyperparameter selection of ensemble models is accomplished by utilizing the gazelle optimization algorithm (GOA) technique. Finally, the Grad-CAM is employed as an XAI technique to enhance transparency by providing human-understandable insights into their decision-making processes. A broad array of experiments using the LXAIOA-ADPCM technique is performed under the Dementia Prediction dataset. The simulation validation of the LXAIOA-ADPCM technique portrayed a superior accuracy output of 95.71% over existing models.
Keywords: Data normalization; Dementia prediction; Explainability artificial intelligence; Feature selection; Gazelle optimization algorithm.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Battineni, G., Chintalapudi, N. & Amenta, F. Machine learning in medicine: Performance calculation of dementia prediction by support vector machines (SVM). Inf. Med. Unlocked16, 100200 (2019).
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

