Focused ultrasound-microbubble treatment arrests the growth and formation of cerebral cavernous malformations
- PMID: 40360762
- PMCID: PMC12354199
- DOI: 10.1038/s41551-025-01390-z
Focused ultrasound-microbubble treatment arrests the growth and formation of cerebral cavernous malformations
Abstract
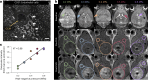
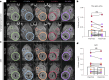
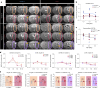
Cerebral cavernous malformations (CCMs) are vascular lesions within the central nervous system that cause debilitating neurological symptoms. Currently, surgical excision and stereotactic radiosurgery, the primary treatment options, pose risks to some patients. Here we tested whether pulsed, low intensity, focused ultrasound-microbubble (FUS-MB) treatments control CCM growth and formation in a clinically representative Krit1 null murine model. FUS-MB under magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) guidance opened the blood-brain barrier, with gadolinium contrast agent deposition most evident at perilesional boundaries. Longitudinal MRI revealed that, at 1 month after treatment, FUS-MB halted the growth of 94% of treated CCMs. In contrast, untreated CCMs grew ~7-fold in volume. FUS-MB-treated CCMs exhibited a marked reduction in Krit1 null endothelial cells. In mice receiving multiple FUS-MB treatments with fixed peak-negative pressures, de novo CCM formation was reduced by 81%, indicating a prophylactic effect. Our findings support FUS-MB as a minimally invasive treatment modality that can safely arrest murine CCM growth and prevent de novo CCM formation in mice. If proven safe and effective in clinical trials, FUS-MB treatment may enhance therapeutic options for CCM patients.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





Update of
-
Focused Ultrasound Blood-Brain Barrier Opening Arrests the Growth and Formation of Cerebral Cavernous Malformations.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Feb 4:2024.01.31.577810. doi: 10.1101/2024.01.31.577810. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Nat Biomed Eng. 2025 Sep;9(9):1531-1546. doi: 10.1038/s41551-025-01390-z. PMID: 38352349 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 EB030744/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- 830909/AHA/American Heart Association-American Stroke Association/United States
- R21NS118278/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- R01 CA279134/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01CA279134/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- R21NS116431/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- 830909/American Heart Association (American Heart Association, Inc.)
- R01 CA226899/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R21 NS116431/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01EB030744/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- R21 NS118278/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EB030409/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- S10 OD025024/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- R01EB030409/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | National Institutes of Health (NIH)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

