A Comprehensive Review: Unraveling the Role of Inflammation in the Etiology of Heart Failure
- PMID: 40360833
- PMCID: PMC12297024
- DOI: 10.1007/s10741-025-10519-w
A Comprehensive Review: Unraveling the Role of Inflammation in the Etiology of Heart Failure
Abstract
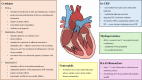
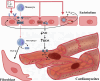
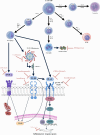
Heart failure (HF) remains a leading cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide, with inflammation playing a pivotal role in its pathogenesis. This comprehensive review aims to elucidate the intricate mechanisms by which inflammation contributes to the development and progression of HF. The review synthesizes current research on the involvement of both innate and adaptive immune responses in HF, highlighting the roles of cytokines, chemokines, and other inflammatory mediators. Recent studies have demonstrated that chronic inflammation, driven by factors such as oxidative stress, neurohormonal activation, and metabolic disturbances, leads to adverse cardiac remodeling and impaired myocardial function. The review explores how systemic inflammation, characterized by elevated levels of inflammatory biomarkers like C-reactive protein (CRP) and interleukin-6 (IL-6), correlates with HF severity and outcomes. Additionally, it discusses the impact of comorbid conditions such as diabetes, obesity, and hypertension on inflammatory pathways and HF risk. The review also delves into the therapeutic implications of targeting inflammation in HF. Despite mixed results from early clinical trials, emerging evidence suggests that anti-inflammatory therapies offer benefits in specific HF phenotypes. The potential of novel therapeutic strategies, including the use of biologics and small molecule inhibitors, is examined in the context of their ability to modulate inflammatory responses and improve clinical outcomes.
Keywords: Biomarkers; Cytokines; Heart Failure; Inflammation; Interleukins.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing Interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

