Trends in the Management of Small HER2-Positive Breast Cancers
- PMID: 40360838
- PMCID: PMC12222400
- DOI: 10.1245/s10434-025-17430-6
Trends in the Management of Small HER2-Positive Breast Cancers
Abstract
Background: The treatment approach for small HER2-positive (+) breast cancers seeks to optimize efficacy while minimizing potential overtreatment and associated toxicities. This study aims to evaluate recent trends in treatment patterns for small HER2+ tumors.
Methods: Patients diagnosed with HER2+, cT1, cN0/pN0 breast cancer treated at a single institution from January 2018 to December 2022 were included. Clinicopathological, treatment, and follow-up data were collected and analyzed.
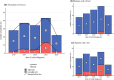
Patients and results: A total of 207 patients were included. Mean age was 63 (± 12.0) years. T category included cT1a in 12.1% (n = 25), cT1b in 28.0% (n = 58), and cT1c in 57.5% (n = 119), while 2.4% (n = 5) had clinical T1 category without further specification. Moreover, 74.4% (n = 154) were hormone receptor positive. Also, 66.7% (n = 138) received adjuvant therapy, 12.6% (n = 26) received neoadjuvant systemic therapy (NAT), and 12.1% (n = 25) received no systemic therapy. Administered regimens included: trastuzumab monotherapy in 6.1% (n = 10), taxane/trastuzumab in 55.5% (n = 91), taxane/carboplatin/trastuzumab in 18.9% (n = 31), and taxane/carboplatin/trastuzumab/pertuzumab in 15.2% (n = 25). In the 26 patients who received NAT, pathological complete response (pCR) was noted in 69.2% (n = 18). Overall, use of NAT increased from 2018 (7.1%) to 2021 (30.2%) and then decreased in 2022 (9.1%). The overall mastectomy rate was 35.3% (n = 73). Young age and multiple tumors were associated with a higher rate of mastectomy (age p < 0.001; multiple tumors p = 0.006). Upstaging of clinically node-negative patients occurred in 14.1% of patients at surgery.
Conclusion: The treatment for cT1N0 HER2+ breast cancers includes primary surgery with adjuvant HER2-targeted therapy in combination with chemotherapy. Primary surgery may allow for an opportunity to deescalate adjuvant therapy with no impact on surgical plan.
Keywords: Adjuvant systemic therapy; Breast cancer; HER2 positive; Neoadjuvant systemic therapy; Treatment patterns.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure: M.K. was consultant and served on advisory boards for AstraZeneca, GE HealthCare, Genentech, Daiichi Sankyo, Gilead, Stemline Therapeutics, Pfizer. M.K. obtained institutional research funding from AstraZeneca. C.M., R.R., and Z.A. declare no conflicts of interest. Ethical Approval: The study was carried out at the Cleveland Clinic and has been approved by the institutional review board (IRB no. 23-1109, date of approval 31 October 2023).
Figures

References
-
- Wolff AC, Hammond MEH, Hicks DG, et al. Recommendations for human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 testing in breast cancer: American Society of Clinical Oncology/College of American Pathologists clinical practice guideline update. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2014;138(2):241–56. 10.5858/arpa.2013-0953-SA. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

