Treatment approach with clinical follow-up in monostotic fibrous dysplasia: a case series
- PMID: 40361161
- PMCID: PMC12070764
- DOI: 10.1186/s13256-025-05261-8
Treatment approach with clinical follow-up in monostotic fibrous dysplasia: a case series
Abstract
Background: Long bones are one of the most common sites involved in fibrous dysplasia. In some cases, there is no deformity, but patients suffer sustained or intermittent dull pain.
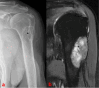
Case presentation: Since 2021, a retrospective case series of seven East Asian patients with fibrous dysplasia of a long bone without severe deformity were reviewed. These patients include three male and four female patients, with an average age of 32.7 years (range 4-70 years). Fibrous dysplasia was diagnosed at a total of three different sites in these seven cases including five femurs (71.4%), one humerus (14.3%), and one fibular bone (14.3%). All patients received treatment with allogenic bone grafting or cortical strut grafting with or without compression locking and screw fixation. The radiological and clinicopathologic presentation was analyzed by the surgeon. There were no cases with polyostotic forms or fibrous dysplasia in combination with extraskeletal disease. The presenting complaint was pain in all cases and localized swelling in 1 (14.3%) of the cases.
Conclusions: Autogenous fibular cortical strut grafting and compression hip screw fixation achieved good postoperative function and provided an early return to work for adult patients with fibrous dysplasia of the femoral neck with mild but prolonged symptoms. However, total hip replacement may be a suitable method for fibrous dysplasia of the femoral neck accompanied by pathological fracture.
Keywords: Allogenic bone grafting; Clinicopathologic presentation; Fibrous dysplasia; Pathological fracture; Radiological presentation; Surgical treatment.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: The study protocol was approved by the institutional review board of Hunan University of Medicine General Hospital, and all medical activities were performed in accordance with approved guidelines and regulations. Consent for publication: Written informed consent was obtained from the patient and/from the patient’s legal guardian for publication of this case report and any accompanying images. A copy of the written consent is available for review by the Editor-in-Chief of this journal. Competing interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures









References
-
- Zhao X, Deng P, Iglesias-Bartolome R, Amornphimoltham P, Steffen DJ, Jin Y, Molinolo AA, de Castro LF, Ovejero D, Yuan Q, Chen Q, Han X, Bai D, Taylor SS, Yang Y, Collins MT, Gutkind JS. Expression of an active Gαs mutant in skeletal stem cells is sufficient and necessary for fibrous dysplasia initiation and maintenance. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018;115(3):E428–37. 10.1073/pnas.1713710115. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

