Changes in Bioactive Constituents in Black Rice Metabolites Under Different Processing Treatments
- PMID: 40361712
- PMCID: PMC12071922
- DOI: 10.3390/foods14091630
Changes in Bioactive Constituents in Black Rice Metabolites Under Different Processing Treatments
Abstract
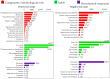
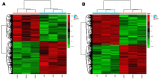
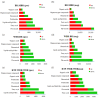
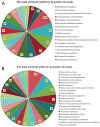
In this study, liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS) was employed to conduct untargeted metabolomics analysis on black rice (BR), milled black rice (MBR), wet germinated black rice (WBR), and high-temperature and high-pressure-treated WBR (HTP-WBR). A total of 6988 positive ions and 7099 negative ions (multiple difference ≥1.2 or ≤0.8333, p < 0.05, and variable importance in projection ≥1) were isolated, and 98 and 100 differential metabolic pathways were identified between the different samples in the positive and negative ion modes, respectively. Distinctive variations in the metabolic compositions of BR, MBR, WBR, and HTP-WBR were observed. Flavonoids, fatty acids, lipids, phenylpropanoids, polyketides, benzenoids, and organooxygen were the dominant differential metabolites. Milling removed the majority of bran-associated bioactive components such as phenolic acids, anthocyanins, micronutrients, fatty acids, antioxidants, and dietary fiber. The germination process significantly reduced the number of flavonoids, polyketides, and lipid-related metabolites, while enzymatic activation notably increased the number of organic acids and amino acids. HTP treatment synergistically enhanced the content of heat-stable flavonoids and polyketides, while simultaneously promoting fatty acid β-oxidation. These findings establish novel theoretical foundations for optimizing processing methodologies and advancing functional characterization in black rice product development.
Keywords: black rice (BR); germination; high temperature and pressure (HTP); metabolomics; milling.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Verma D.K., Srivastav P.P. Bioactive compounds of rice (Oryza sativa L.): Review on paradigm and its potential benefit in human health. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020;97:355–365. doi: 10.1016/j.tifs.2020.01.007. - DOI
-
- Astuti L., Almasyhuri A., Dian S. Pengaruh Proses Pemasakan terhadap Komposisi Zat Gizi Bahan Pangan Sumber Protein. Media Penelit. Dan Pengemb. Kesehat. 2015;25:235–242.
-
- Chen X., Tao Y., Ali A., Zhuang Z., Guo D., Guo Q., Riaz A., Zhang H., Xu P., Liao Y., et al. Transcriptome and Proteome Profiling of Different Colored Rice Reveals Physiological Dynamics Involved in the Flavonoid Pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019;20:2463. doi: 10.3390/ijms20102463. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

