Drug Resistance Analysis of Pancreatic Cancer Based on Universally Differentially Expressed Genes
- PMID: 40362181
- PMCID: PMC12071644
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26093936
Drug Resistance Analysis of Pancreatic Cancer Based on Universally Differentially Expressed Genes
Abstract
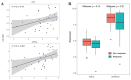
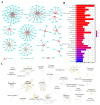
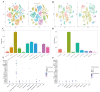
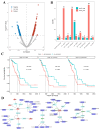
The high heterogeneity between patients can complicate the diagnosis and treatment of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC). Here, we explored the association of universally differentially expressed genes (UDEGs) with resistance to chemotherapy and immunotherapy in the context of pancreatic cancer. In this work, sixteen up-regulated and three down-regulated genes that were dysregulated in more than 85% of 102 paired and 5% of 521 unpaired PDAC samples were identified and defined as UDEGs. A single-cell level analysis further validated the high expression levels of the up-UDEGs and the low levels of the down-UDEGs in cancer-related ductal cells, which could represent the malignant changes seen in pancreatic cancer. Based on a drug sensitivity analysis, we found that ANLN, GPRC5A and SERPINB5 are closely related to the resistance mechanism of PDAC, and their high expression predicted worse survival for PDAC patients. This suggests that targeting these genes could be a potential way to reduce drug resistance and improve survival. Based on the immune infiltration analysis, the abnormal expression of the UDEGs was found to be related to the formation of an immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment. In conclusion, these UDEGs are common features of PDAC and could be involved in the resistance of pancreatic cancer and might serve as novel drug targets to guide research into drug repurposing.
Keywords: drug resistance; immunity; pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma; universally differentially expressed genes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Deciphering the Prognostic Implications of the Components and Signatures in the Immune Microenvironment of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma.Front Immunol. 2021 Mar 10;12:648917. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.648917. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33777046 Free PMC article.
-
SCNrank: spectral clustering for network-based ranking to reveal potential drug targets and its application in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.BMC Med Genomics. 2020 Apr 3;13(Suppl 5):50. doi: 10.1186/s12920-020-0681-6. BMC Med Genomics. 2020. PMID: 32241274 Free PMC article.
-
Single-cell transcriptome analysis reveals subtype-specific clonal evolution and microenvironmental changes in liver metastasis of pancreatic adenocarcinoma and their clinical implications.Mol Cancer. 2024 May 3;23(1):87. doi: 10.1186/s12943-024-02003-0. Mol Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38702773 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic trends in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC).Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2019 Feb;28(2):161-177. doi: 10.1080/13543784.2019.1557145. Epub 2018 Dec 16. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2019. PMID: 30539678 Review.
-
Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC): clinical progress in the last five years.Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2025 Mar;34(3):149-160. doi: 10.1080/13543784.2025.2473698. Epub 2025 Mar 4. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2025. PMID: 40012027 Review.
Cited by
-
In Vitro Evaluation of Electrochemotherapy Combined with Sotorasib in Pancreatic Carcinoma Cell Lines Harboring Distinct KRAS Mutations.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jul 24;26(15):7165. doi: 10.3390/ijms26157165. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40806294 Free PMC article.
References
-
- He J., Blair A.B., Groot V.P., Javed A.A., Burkhart R.A., Gemenetzis G., Hruban R.H., Waters K.M., Poling J., Zheng L., et al. Is a Pathological Complete Response Following Neoadjuvant Chemoradiation Associated With Prolonged Survival in Patients With Pancreatic Cancer? Ann. Surg. 2018;268:1–8. doi: 10.1097/SLA.0000000000002672. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chuong M.D., Springett G.M., Freilich J.M., Park C.K., Weber J.M., Mellon E.A., Hodul P.J., Malafa M.P., Meredith K.L., Hoffe S.E., et al. Stereotactic body radiation therapy for locally advanced and borderline resectable pancreatic cancer is effective and well tolerated. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2013;86:516–522. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2013.02.022. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

