Identification of Potential Prophylactic Medical Countermeasures Against Acute Radiation Syndrome (ARS)
- PMID: 40362293
- PMCID: PMC12072061
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26094055
Identification of Potential Prophylactic Medical Countermeasures Against Acute Radiation Syndrome (ARS)
Abstract
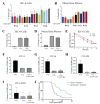
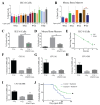
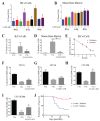
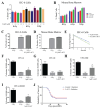
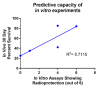
Acute radiation syndrome (ARS) occurs when hematopoietic or gastrointestinal cells are damaged by radiation exposure causing DNA damage to the bone marrow and gastrointestinal epithelial stem cell populations. In these highly proliferative cell types, DNA damage inhibits stem cell repopulation. In humans and animals, this inability to regenerate stem cells is lethal. Within this manuscript, several compounds, Amifostine, Captopril, Ciprofloxacin, PrC-210, 5-AED (5-androstene-3β,17β-diol), and 5-AET (5-androstene-3β,7β,17B-triol), are assessed for their ability to protect against ARS in an in vitro and/or in vivo setting. ARS was accomplished by irradiating mouse bone marrow cells or rat intestinal epithelial (IEC-6) cells in vitro with 4-8 Gy and in vivo by exposing Mus musculus to 7.3 Gy of whole-body irradiation. The primary endpoints of this study include cellular viability, DNA damage via γ-H2AX, colony formation, and overall survival at 30-days post-irradiation. In addition to evaluating the radioprotective performance of each compound, this study establishes a distinct set of in vitro assays to predict the overall efficacy of potential radioprotectors in an in vivo model of ARS. Furthermore, these results highlight the need for FDA-approved medical intervention to protect against ARS.
Keywords: DNA damage; acute radiation syndrome; radioprotection.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Hall E.J., Giaccia A.J. Radiobiology for the Radiologist. 6th ed. Lippincott Williams and Wilkins; Philadellphia, PA, USA: 2006.
-
- Indo H.P., Inanami O., Koumura T., Suenaga S., Yen H.-C., Kakinuma S., Matsumoto K.-I., Nakanishi I., Clair W.S., Clair D.K.S., et al. Roles of mitochondria-generated reactive oxygen species on X-ray-induced apoptosis in a human hepatocellular carcinoma cell line, HLE. Free Radic. Res. 2012;46:1029–1043. doi: 10.3109/10715762.2012.698012. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

