Targeting Metabolism: Innovative Therapies for MASLD Unveiled
- PMID: 40362316
- PMCID: PMC12071536
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26094077
Targeting Metabolism: Innovative Therapies for MASLD Unveiled
Abstract
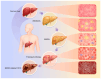
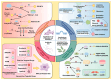
The recent introduction of the term metabolic-dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) has highlighted the critical role of metabolism in the disease's pathophysiology. This innovative nomenclature signifies a shift from the previous designation of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), emphasizing the condition's progressive nature. Simultaneously, MASLD has become one of the most prevalent liver diseases worldwide, highlighting the urgent need for research to elucidate its etiology and develop effective treatment strategies. This review examines and delineates the revised definition of MASLD, exploring its epidemiology and the pathological changes occurring at various stages of the disease. Additionally, it identifies metabolically relevant targets within MASLD and provides a summary of the latest metabolically targeted drugs under development, including those in clinical and some preclinical stages. The review finishes with a look ahead to the future of targeted therapy for MASLD, with the goal of summarizing and providing fresh ideas and insights.
Keywords: MASLD; inflammatory response; lipidosis; metabolic syndrome; targeted therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Man S., Deng Y., Ma Y., Fu J., Bao H., Yu C., Lv J., Liu H., Wang B., Li L. Prevalence of Liver Steatosis and Fibrosis in the General Population and Various High-Risk Populations: A Nationwide Study with 5.7 Million Adults in China. Gastroenterology. 2023;165:1025–1040. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2023.05.053. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

