Revisiting Secondary Dilative Cardiomyopathy
- PMID: 40362416
- PMCID: PMC12071311
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26094181
Revisiting Secondary Dilative Cardiomyopathy
Abstract
Secondary dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM) refers to left ventricular dilation and impaired systolic function arising from identifiable extrinsic causes, such as ischemia, hypertension, toxins, infections, systemic diseases, or metabolic disorders. Unlike primary DCM, which is predominantly genetic, secondary DCM represents a diverse spectrum of pathophysiological mechanisms linked to external insults on myocardial structure and function. The increasing prevalence of conditions such as alcohol use disorder, chemotherapy-induced cardiotoxicity, and viral myocarditis underscores the need for heightened awareness and early recognition of secondary DCM. A comprehensive analysis of clinical trial data and observational studies involving secondary dilative cardiomyopathy was conducted, with a focus on mortality, symptom relief, and major adverse events. A systematic literature review was performed using databases, including PubMed, Embase, and ClinicalTrials.gov, following PRISMA guidelines for study selection. Data were extracted on patient demographics, etiology of dilation, trial design, outcomes, and follow-up duration. Advances in diagnostic modalities have refined the ability to identify underlying causes of secondary DCM. For example, high-sensitivity troponin and cardiac magnetic resonance imaging are pivotal in diagnosing myocarditis and differentiating it from ischemic cardiomyopathy. Novel insights into toxin-induced cardiomyopathies, such as those related to anthracyclines and immune checkpoint inhibitors, have highlighted pathways of mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress. Treatment strategies emphasize the management of the causing condition alongside standard heart failure therapies, including RAAS inhibitors and beta-blockers. Emerging therapies, such as myocardial recovery protocols in peripartum cardiomyopathy and immune-modulating treatments in myocarditis, are promising in reversing myocardial dysfunction. Secondary DCM encompasses a heterogeneous group of disorders that require a precise etiological diagnosis for effective management. Timely identification and treatment of the underlying cause, combined with optimized heart failure therapies, can significantly improve outcomes. Future research focuses on developing targeted therapies and exploring the role of biomarkers and precision medicine in tailoring treatment strategies for secondary DCM.
Keywords: biomarkers; dilative cardiomyopathy; precision medicine; targeted therapies.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
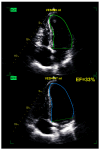
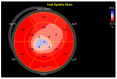

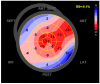
References
-
- Brieler J., Breeden M.A., Tucker J. Cardiomyopathy: An Overview. Am. Fam. Physician. 2017;96:640–646. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

