Unlocking the Pharmacological Potential of Myricetin Against Various Pathogenesis
- PMID: 40362425
- PMCID: PMC12071824
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26094188
Unlocking the Pharmacological Potential of Myricetin Against Various Pathogenesis
Abstract
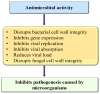
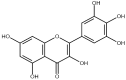
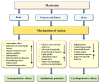
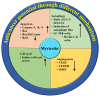
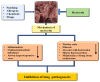
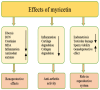
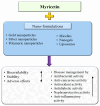
Myricetin is a natural flavonoid with powerful antioxidant and anti-inflammatory potential commonly found in vegetables, fruits, nuts, and tea. The vital role of this flavonoid in the prevention and treatment of various diseases is evidenced by its ability to reduce inflammation and oxidative stress, maintain tissue architecture, and modulate cell signaling pathways. Thus, this review summarizes recent evidence on myricetin, focusing precisely on its mechanisms of action in various pathogenesis, including obesity, diabetes mellitus, arthritis, osteoporosis, liver, neuro, cardio, and reproductive system-associated pathogenesis. Moreover, it has been revealed that myricetin exhibits anti-microbial properties due to obstructive virulence factors, preventing biofilm formation and disrupting membrane integrity. Additionally, synergistic potential with other drugs and the role of myricetin-based nanoformulations in different diseases are properly discussed. This review seeks to increase the understanding of myricetin's pharmacological potential in various diseases, principally highlighting its effective mechanisms of action. Further wide-ranging research, as well as more randomized and controlled clinical trial studies, should be executed to reconnoiter this compound's therapeutic value, safety, and usefulness against various human pathogenesis.
Keywords: inflammation; myricetin; nanoformulation; oxidative stress; pathogenesis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Unveiling myricetin's pharmacological potency: A comprehensive exploration of the molecular pathways with special focus on PI3K/AKT and Nrf2 signaling.J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2024 Jun;38(6):e23739. doi: 10.1002/jbt.23739. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2024. PMID: 38769721 Review.
-
Pharmacological Potential of Kaempferol, a Flavonoid in the Management of Pathogenesis via Modulation of Inflammation and Other Biological Activities.Molecules. 2024 Apr 26;29(9):2007. doi: 10.3390/molecules29092007. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 38731498 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anti-inflammatory and anti-allergic potential of dietary flavonoids: A review.Biomed Pharmacother. 2022 Dec;156:113945. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2022.113945. Epub 2022 Oct 31. Biomed Pharmacother. 2022. PMID: 36411631 Review.
-
Myricetin: A Significant Emphasis on Its Anticancer Potential via the Modulation of Inflammation and Signal Transduction Pathways.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jun 2;24(11):9665. doi: 10.3390/ijms24119665. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37298616 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Flavonoid Myricetin as Potent Anticancer Agent: A Possibility towards Development of Potential Anticancer Nutraceuticals.Chin J Integr Med. 2024 Jan;30(1):75-84. doi: 10.1007/s11655-023-3701-5. Epub 2023 Jun 21. Chin J Integr Med. 2024. PMID: 37340205 Review.
Cited by
-
Plant-based flavonoids and their nanoparticles: Latest arsenal against Alzheimer's disease.Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2025 Jun 30. doi: 10.1007/s13346-025-01906-9. Online ahead of print. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2025. PMID: 40587047 Review.
References
-
- van Wyk A., Prinsloo G. Medicinal plant harvesting, sustainability and cultivation in South Africa. Biol. Conserv. 2018;227:335–342. doi: 10.1016/j.biocon.2018.09.018. - DOI
-
- Torres-León C., Ramírez F.R., Aguirre-Joya J.A., Ramírez-Moreno A., Chávez-González M.L., Aguillón-Gutierrez D.R., Camacho-Guerra L., Ramírez-Guzmán N., Vélez S.H., Aguilar C.N. Medicinal plants used by rural communities in the arid zone of Viesca and Parras Coahuila in northeast Mexico. Saudi Pharm. J. 2023;31:21–28. doi: 10.1016/j.jsps.2022.11.003. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization (WHO) World Health Organization Traditional Medicine Strategy 2014–2023. WHO; Geneva, Switzerland: 2013. pp. 1–78.
-
- Atanasov A.G., Waltenberger B., Pferschy-Wenzig E.-M., Linder T., Wawrosch C., Uhrin P., Temml V., Wang L., Schwaiger S., Heiss E.H., et al. Discovery and resupply of pharmacologically active plant-derived natural products: A review. Biotechnol. Adv. 2015;33:1582–1614. doi: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2015.08.001. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

