Crosstalk Among Gut Microbiota, Fecal Metabolites, and Amygdala Neuropathology Genes After Ginger Polyphenol Administration in Female Rats with Neuropathic Pain: Evidence for Microbiota-Gut-Brain Connection
- PMID: 40362753
- PMCID: PMC12073668
- DOI: 10.3390/nu17091444
Crosstalk Among Gut Microbiota, Fecal Metabolites, and Amygdala Neuropathology Genes After Ginger Polyphenol Administration in Female Rats with Neuropathic Pain: Evidence for Microbiota-Gut-Brain Connection
Abstract
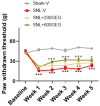
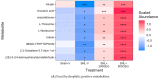
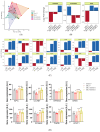
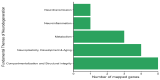
Objectives. The relationships among neuropathic pain, gut microbiota, microbiome-derived metabolites, and neuropathology have received increasing attention. This study examined the effects of two dosages of gingerol-enriched ginger (GEG) on mechanical hypersensitivity, anxiety-like behavior, gut microbiome composition and its metabolites, and neuropathology markers in female rats in the spinal nerve ligation (SNL) model of neuropathic pain. Methods. Forty female rats were assigned to 4 groups: sham-vehicle, SNL-vehicle, SNL+GEG at 200 mg/kg BW, and SNL+GEG at 600 mg/kg BW via oral gavage. All animals were given an AIN-93G diet for 5 weeks. Mechanical hypersensitivity was assessed by the von Frey test. Anxiety-like behavior was assessed by the open field test. Fecal microbiota composition and metabolites were determined using 16S rRNA gene sequencing and GC-MS, respectively. Neuropathology gene expression profiling of the amygdala was assessed by an nCounter® Neuropathology pathway panel. Results. Both GEG-treated groups showed decreased mechanical hypersensitivity and anxiety-like behavior in the SNL model. Gut microbiome diversity in both GEG groups was decreased compared with untreated SNL rats. In the SNL model, phyla such as Bacteroidota, Proteobacteria and Verrucomicrobiota were decreased. Compared with the untreated SNL group, both GEG groups exhibited increased abundance of the phyla Bacteroidota (i.e., Rikenella, Alistipes, Muribaculaceae, Odoribacter), Firmicutes (i.e., UBA1819, Ruminococcaceae, Oscillospiraceae, Roseburia), and Verrucomicrobiota (i.e., Victivallis). GEG groups had higher levels of nine hydrophilic positive metabolites [val-glu, urocanic acid, oxazolidinone, L-threonine, L-norleucine, indole, imino-tryptophan, 2,3-octadiene-5,7-diyn-1-ol, and (2E)-3-(3-hydroxyphenyl) acrylaldehyde] and two hydrophilic negative metabolites [methylmalonic acid and metaphosphoric acid], as well as lower levels of five hydrophilic metabolites [xanthine, N-acetylmuramic acid, doxaprost, adenine, and 1-myristoyl-2-oleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine]. Among the 770 neuropathology genes, 1 gene (PLA2G4A) was upregulated and 2 genes (CDK5R1 and SHH) were downregulated in SNL rats. GEG caused the upregulation of nine genes (APC, CCNH, EFNA5, GRN, HEXB, ITPR1, PCSK2, TAF9, and WFS1) and downregulation of three genes (AVP, C4A, and TSPO) in the amygdala. Conclusions. GEG supplementation mitigated pain-associated behaviors in female rats with neuropathic pain, in part by reversing the molecular neuropathology signature of the amygdala. This was associated with changes in the gut microbiome composition and fecal metabolites, which could play a role in mediating the effects of GEG on neuropathic pain.
Keywords: brain; ginger; gut microbiome; neuropathic pain; neuropathology; rats.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
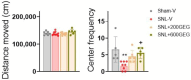


References
-
- Shen C.L., Wang R., Ji G.C., Elmassry M.M., Zabet-Moghaddam M., Vellers H., Hamood A.N., Gong X.X., Mirzaei P., Sang S.M., et al. Dietary supplementation of gingerols- and shogaols-enriched ginger root extract attenuate pain-associated behaviors while modulating gut microbiota and metabolites in rats with spinal nerve ligation. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2022;100:108904. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2021.108904. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Shen C.L., Wang R., Santos J.M., Elmassry M.M., Stephens E., Kim N., Neugebauer V. Ginger alleviates mechanical hypersensitivity and anxio-depressive behavior in rats with diabetic neuropathy through beneficial actions on gut microbiome composition, mitochondria, and neuroimmune cells of colon and spinal cord. Nutr. Res. 2024;124:73–84. doi: 10.1016/j.nutres.2024.01.014. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

