(-)-Oleuropein as a Novel Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer Progression and Recurrence Suppressor via Targeting PCSK9-LDLR Axis
- PMID: 40362754
- PMCID: PMC12073333
- DOI: 10.3390/nu17091445
(-)-Oleuropein as a Novel Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer Progression and Recurrence Suppressor via Targeting PCSK9-LDLR Axis
Abstract
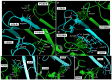
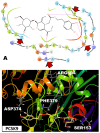
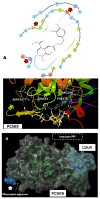
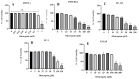
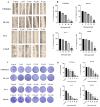
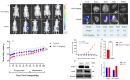
Background/Objectives: Prostate cancer (PC) is among the most common malignancy in men. Several newly diagnosed patients have a locally advanced disease and distant metastasis at the initial diagnosis time. Castration-resistant PC (CRPC) patients have 100% recurrence incidence despite completing a therapeutic regimen, leading to high mortality. Androgen deprivation therapy and androgen inhibitors are initially effective, but resistance is inevitably developed. Epidemiological studies indicated that the Mediterranean diet, with high olive phenolic contents, is associated with a lower incidence of certain malignancies. This study aims at exploring the mCRPC progression and recurrence-suppressive and molecular effects of the major olive leaf phenolic glucoside (-)-oleuropein (OLE). Results: OLE downregulated the levels of proprotein convertase subtlisin/klexin type 9 (PCSK9) and normalized the low-density lipoprotein receptor (LDLR) in PC cells in vitro. Thus, a PCSK9-LDLR protein-protein interaction (PPI) in silico model was generated and used to assess OLE and its aglycone (OA) ability to bind at PCSK9 and thereby interfere with PCSK9-LDLR PPI. OLE perfectly filled the PCSK9 interface versus OA. Both OLE and OA showed virtual potential to interfere with PCSK9-LDLR PPI. OLE showed modest in vitro viability, migration, and clonogenicity suppressive effects on diverse human PC cell lines. OLE effectively suppressed mCRPC progression and recurrence in a nude mouse xenograft model. RNA-sequencing results proved the PCSK1, PCSK2, and PCSK9 downregulation in OLE-treated recurrent tumors versus vehicle control. Conclusions: Oleuropein is a novel lead useful for the control of mCRPC progression and the prevention of its recurrence via targeting PCSK9 expression and PPI with LDLR.
Keywords: PCSK9-LDLR; metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer; oleuropein; olive phenolics; protein–protein interaction; recurrence.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Giacinti S., Poti G., Roberto M., Macrini S., Bassanelli M., DI Pietro F., Aschelter A.M., Ceribelli A., Ruggeri E.M., Marchetti P. Molecular basis of drug resistance and insights for new treatment approaches in mCRPC. Anticancer. Res. 2018;38:6029–6039. doi: 10.21873/anticanres.12953. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

