Efficient Gearbox Fault Diagnosis Based on Improved Multi-Scale CNN with Lightweight Convolutional Attention
- PMID: 40363076
- PMCID: PMC12073503
- DOI: 10.3390/s25092636
Efficient Gearbox Fault Diagnosis Based on Improved Multi-Scale CNN with Lightweight Convolutional Attention
Abstract
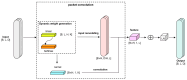
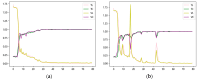
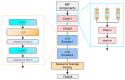
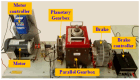
As a core transmission component of modern industrial equipment, the operation status of the gearbox has a significant impact on the reliability and service life of major machinery. In this paper, we propose an intelligent diagnosis framework based on Empirical Mode Decomposition and multimodal feature co-optimization and innovatively construct a fault diagnosis model by fusing a multi-scale convolutional neural network and a lightweight convolutional attention model. The framework extracts the multi-band features of vibration signals through the improved multi-scale convolutional neural network, which significantly enhances adaptability to complex working conditions (variable rotational speed, strong noise); at the same time, the lightweight convolutional attention mechanism is used to replace the multi-attention of the traditional Transformer, which greatly reduces computational complexity while guaranteeing accuracy and realizes highly efficient, lightweight local-global feature modeling. The lightweight convolutional attention is adaptively captured by the dynamic convolutional kernel generation strategy to adaptively capture local features in the time domain, and combined with grouped convolution to enhance the computational efficiency further; in addition, parameterized revised linear units are introduced to retain fault-sensitive negative information, which enhances the model's ability to detect weak faults. The experimental findings demonstrate that the proposed model achieves an accuracy greater than 98.9%, highlighting its exceptional diagnostic accuracy and robustness. Moreover, compared to other fault diagnosis methods, the model exhibits superior performance under complex working conditions.
Keywords: EMD; dynamic convolutional kernel; gearbox fault diagnosis; lightweight convolutional attention; multi-scale CNN.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures









References
-
- Bai Y., Cheng W., Wen W., Liu Y. Application of Time-Frequency Analysis in Rotating Machinery Fault Diagnosis. Shock Vib. 2023;2023:9878228. doi: 10.1155/2023/9878228. - DOI
-
- Xu Y., Liu J., Wan Z., Zang D., Jiang D. Rotor fault diagnosis using domain-adversarial neural network with time-frequency analysis. Machines. 2022;10:610. doi: 10.3390/machines10080610. - DOI
-
- Shi J., Peng D., Peng Z., Zhang Z., Goebel K., Wu D. Planetary gearbox fault diagnosis using bidirectional-convolutional LSTM networks. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2022;162:107996. doi: 10.1016/j.ymssp.2021.107996. - DOI
-
- Guo Y., Zhou J., Dong Z., She H., Xu W. Research on bearing fault diagnosis based on novel MRSVD-CWT and improved CNN-LSTM. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2024;35:095003. doi: 10.1088/1361-6501/ad4fb3. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

