A Low-Cost pH Sensor for Real-Time Monitoring of Aquaculture Systems in a Multi-Layer Wireless Sensor Network
- PMID: 40363260
- PMCID: PMC12074378
- DOI: 10.3390/s25092824
A Low-Cost pH Sensor for Real-Time Monitoring of Aquaculture Systems in a Multi-Layer Wireless Sensor Network
Abstract
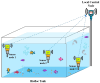
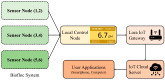
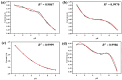
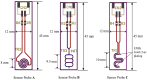
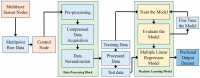
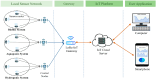
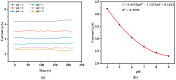
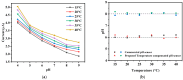
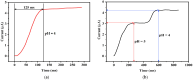
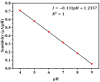
For aquaculture systems, pH is the prime quality indicator and is highly related to other water quality indicators like ammonia and ammonium ions. The available pH sensors using chemical references are not suitable for continuous in situ monitoring of aquaculture systems due to their frequent calibration requirement and high cost. This research develops a pH sensor with temperature compensation implementing a machine learning (ML) algorithm. Unlike traditional methods, this sensor utilizes electronic calibration, eliminating the need for chemical calibration and ongoing maintenance efforts. The application of this low-cost sensor is particularly well suited for in situ aquaculture scenarios, where multiple local sensor nodes operate under the control of a master node. The test results of the developed sensor show an improved sensitivity from 0.288 µA/pH to 0.316 µA/pH compared to the available pH sensors. Additionally, the response time has been improved from 1 s to 125 ms, showcasing the suitability of this pH sensor for real-time water quality monitoring of aquaculture applications.
Keywords: aquaculture; electrode; pH sensor; temperature compensation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Halim M.A., Nahar S., Nabi M.M. Biofloc Technology in Aquaculture and Its Potentiality: A Review. Int. J. Fish. Aquat. Stud. 2019;7:260–266.
-
- Vivaldi F., Salvo P., Poma N., Bonini A., Biagini D., Del Noce L., Melai B., Lisi F., Di Francesco F. Recent Advances in Optical, Electrochemical and Field Effect PH Sensors. Chemosensors. 2021;9:33. doi: 10.3390/chemosensors9020033. - DOI
-
- Schmidt J., Ithuralde R.E. A New Teaching Laboratory Experiment to Address the Effect of PH on Solubility. Chem. Educ. 2017;22:70–72.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

