CD44 Receptor-Mediated Ferroptosis Induction by Hyaluronic Acid Carbon Quantum Dots in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells Through Downregulation of SLC7A11 Pathway
- PMID: 40363642
- PMCID: PMC12073876
- DOI: 10.3390/ma18092139
CD44 Receptor-Mediated Ferroptosis Induction by Hyaluronic Acid Carbon Quantum Dots in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells Through Downregulation of SLC7A11 Pathway
Abstract
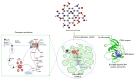
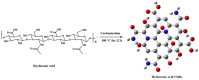
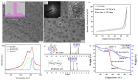
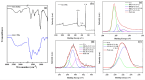
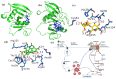
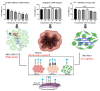
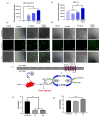
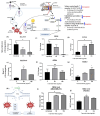
The field of cancer therapy is actively pursuing highly effective self-targeted drug delivery materials endowed with exceptional properties. Recently, hyaluronic acid (HA), a naturally occurring polysaccharide, has been recognized as a potential target ligand for CD44 receptors, which are frequently expressed on various solid tumor cells targeted in cancer therapy. HA carbon quantum dots (CQDs) exhibit several advantageous properties, including a high surface area-to-volume ratio, small particle size, biocompatibility, and low cytotoxicity, making them ideal for biomedical applications, such as CD44-targeted drug delivery in ferroptosis-based cancer therapy. In this study, we synthesized HA-CQDs to enhance CD44-mediated ligand-receptor interactions targeting triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC). CQDs facilitate the intracellular generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS), leading to glutathione depletion. These processes result in crucial actions such as the downregulation of glutathione peroxidase 4, downregulation of solute carrier family 7 member 11, and inhibition of cystine intake. The subsequent intracellular ROS, originating from lipid peroxidation, induces ferroptosis. Our HA-CQDs engage CD44 receptors, selectively targeting TNBCs and enhancing cancer recognition. This interaction potentially enhances the nanoplatform-based CD44 targeted therapeutic effects in inducing ferroptosis.
Keywords: carbon quantum dots (CQDs); ferroptosis; glutathione depletion; hyaluronic acid (HA); lipid peroxidation; reactive oxygen species (ROS).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

